High Similarity Image Recognition and Classification Algorithm Based on Convolutional Neural Network
- PMID: 35449738
- PMCID: PMC9018201
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2836486
High Similarity Image Recognition and Classification Algorithm Based on Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
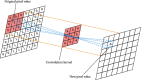
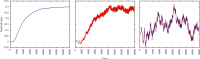
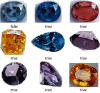
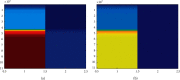
Nowadays, the information processing capabilities and resource storage capabilities of computers have been greatly improved, which also provides support for the neural network technology. Convolutional neural networks have good characterization capabilities in computer vision tasks, such as image recognition technology. Aiming at the problem of high similarity image recognition and classification in a specific field, this paper proposes a high similarity image recognition and classification algorithm fused with convolutional neural networks. First, we extract the image texture features, train different types, and different resolution image sets and determine the optimal texture different parameter values. Second, we decompose the image into subimages according to the texture difference, extract the energy features of each subimage, and perform classification. Then, the input image feature vector is converted into a one-dimensional vector through the alternating 5-layer convolution and 3-layer pooling of convolutional neural networks. On this basis, different sizes of convolution kernels are used to extract different convolutions of the image features, and then use convolution to achieve the feature fusion of different dimensional convolutions. Finally, through the increase in the number of training and the increase in the amount of data, the network parameters are continuously optimized to improve the classification accuracy in the training set and in the test set. The actual accuracy of the weights is verified, and the convolutional neural network model with the highest classification accuracy is obtained. In the experiment, two image data sets of gems and apples are selected as the experimental data to classify and identify gems and determine the origin of apples. The experimental results show that the average identification accuracy of the algorithm is more than 90%.
Copyright © 2022 Zhizhe Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




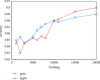
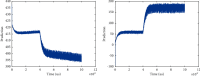
References
-
- Wang P., Wang J., Li Y., Li P., Li L., Jiang M. Automatic classification of breast cancer histopathological images based on deep feature fusion and enhanced routing. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control . 2021;65 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102341.102341 - DOI
-
- Gayathri S., Gopi V. P., Palanisamy P. A lightweight CNN for Diabetic Retinopathy classification from fundus images. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control . 2020;62:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102115. - DOI
-
- Wei H., Zhu M., Wang B., Wang J., Sun D. Two-level progressive attention convolutional network for fine-grained image recognition. IEEE Access . 2020;8:104985–104995. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.2999722. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

