The Utilization of Chinese Herbal Products for Hyperthyroidism in National Health Insurance System (NHIRD) of Taiwan: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 35449810
- PMCID: PMC9017513
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5500604
The Utilization of Chinese Herbal Products for Hyperthyroidism in National Health Insurance System (NHIRD) of Taiwan: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
Background: Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) relieves associated symptoms of hyperthyroidism such as heat intolerance, palpitations, tremor, anxiety, weight loss, increased frequency of bowel movements, and shortness of breath. However, there are no studies regarding the core prescription patterns of herbal formula and single herbs for hyperthyroidism in Taiwan.
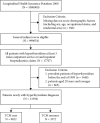
Materials and methods: This is a retrospective, observational study using the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) in Taiwan to analyze the prescription patterns of TCM. Demographic factors, such as sex, age, occupational status, and residential area, and the risk factors for hyperthyroidism were also studied.
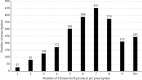
Results: The outpatient or/and inpatient services for hyperthyroidism receive 17,707 cases in a year. Overall, there were 13,394 newly diagnosed patients. TCM was used in 73% of the patients, and 77.3% of the patients were females. The acceptability of TCM was higher among female patients. Most patients were diagnosed with hyperthyroidism between the ages of 30 and 49 years. The most common comorbidity identified was diabetes mellitus. The most commonly prescribed Chinese herbal product (CHP) formula was Jia-Wei-Xia-Yao-San, while Xia-Ku-Cao was the most commonly prescribed single CHP. There was a high coprescription rate for Xuan-Shen, Bei-Mu, and Mu-Li.
Conclusion: This study describes the core prescription pattern of TCM used in the treatment of patients with hyperthyroidism in Taiwan. The most frequently used CHPs could be potential candidates for future pharmacologic studies or clinical trials.
Copyright © 2022 Cheng-Chieh Chang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription patterns of Chinese herbal products for post-surgery colon cancer patients in Taiwan.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):702-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.06.012. Epub 2014 Jun 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24945402
-
Prescription patterns of Chinese herbal products for patients with sleep disorder and major depressive disorder in Taiwan.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Aug 2;171:307-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.05.045. Epub 2015 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26068429
-
Prescription pattern of Chinese herbal products for heart failure in Taiwan: A population-based study.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Feb 1;228:90-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.172. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27863367
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Induced Liver Injury.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2014 Jun;2(2):80-94. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2014.00003. Epub 2014 Jun 15. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 26357619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Herbs for Breast Cancer Prevention and Survival: A Narrative Review of Epidemiological Studies from Taiwan.Curr Oncol Rep. 2024 Nov;26(11):1321-1333. doi: 10.1007/s11912-024-01595-6. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Curr Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39361077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MACE and Hyperthyroidism Treated With Medication, Radioactive Iodine, or Thyroidectomy.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Mar 4;7(3):e240904. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.0904. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38436957 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Xiaoyao-san preparations in treating Hashimoto's thyroiditis: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 13;16:1528506. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1528506. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40584613 Free PMC article.
-
Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation.Open Life Sci. 2023 Jul 19;18(1):20220638. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0638. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37483425 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and potential mechanism of Jiawei-Xiaoyao-San for hyperthyroidism: a systematic review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 13;14:1241962. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1241962. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37780612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Leo S., Braverman L. E. The Thyroid and its Diseases . Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2019. Iodine-induced thyroid dysfunction; pp. 435–452. - DOI
-
- Liang Y. L., Guo H. R. The Epidemiology of Hyperthyroidism In Taiwan. Institute Of Clinical Medicine . Vol. 32. Tainan City, Taiwan: National Cheng Kung University; 2013.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

