Health-Related Quality of Life and Its Related Factors in Survivors of Stroke in Rural China: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 35450122
- PMCID: PMC9016152
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.810185
Health-Related Quality of Life and Its Related Factors in Survivors of Stroke in Rural China: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Stroke is a major health threat and the leading cause of mortality and disability in China. The aims of this study were to identify the possible influencing factors of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and its domain-specific contents in stroke patients in rural areas in China.
Methods: A total of 1,709 stroke patients aged 36-79 years from the baseline data of Henan Rural Cohort study (n = 39,259) were included in the cross-sectional study. The Chinese version of the European Quality of Life Five Dimension (including mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression) Five Level Scale (EQ-5D-5L) and visual analog scale (VAS) were used to evaluate HRQoL in stroke patients. Tobit regression models, generalized linear models and binary logistic regression models were constructed to determine potential influencing factors of the EQ-5D utility index, as well as influencing factors of each domain and VAS score.
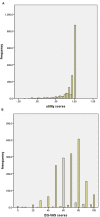
Results: The mean utility index and VAS scores of stroke patients were 0.885 (SD, 0.204), and 68.39 (SD, 17.31), respectively. Pain/discomfort (PD, 35.2%) and mobility (MO, 30.4%) were the most frequently reported issues. Regression models revealed that illiterate; a low monthly income; low physical activity intensity; and diabetes, anxiety, depression, or poor sleep quality were significantly associated with lower utility index and VAS scores among stroke patients. In addition, patients with stroke who were older, female, drinking, smoking, and consuming a high-fat diet, had a higher BMI, and lived with a stroke for a longer time, were also significantly associated with different dimensions of the EQ-5D.
Conclusion: Patients with stroke in rural areas in China had a low HRQoL. Factors associated with the EQ-5D utility index as well as each domain and VAS score, need to be considered by health providers in rural areas. Patients with stroke in rural areas need to be included in national basic public medical services and managed systematically by medical institutions.
Keywords: EQ-5D-5L; HRQoL; influencing factors; rural; stroke.
Copyright © 2022 Mei, Zhang, Wu, Hou, Liu, Sang, Mao, Zhang, Yang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

