Vaccine-induced and naturally-acquired protection against Omicron and Delta symptomatic infection and severe COVID-19 outcomes, France, December 2021 to January 2022
- PMID: 35451363
- PMCID: PMC9027152
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.16.2200250
Vaccine-induced and naturally-acquired protection against Omicron and Delta symptomatic infection and severe COVID-19 outcomes, France, December 2021 to January 2022
Erratum in
-
Author's correction for Euro Surveill. 2022;27(16).Euro Surveill. 2022 Apr;27(17):220428c. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.17.220428c. Euro Surveill. 2022. PMID: 35485268 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
We assessed the protection conferred by naturally-acquired, vaccine-induced and hybrid immunity during the concomitant Omicron and Delta epidemic waves in France on symptomatic infection and severe COVID-19. The greatest levels of protection against both variants were provided by hybrid immunity. Protection against Omicron symptomatic infections was systematically lower and waned at higher speed than against Delta in those vaccinated. In contrast, there were little differences in variant-specific protection against severe inpatient outcomes in symptomatic individuals.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; Test negative design; immunity; vaccination effectiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
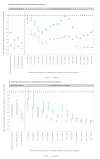
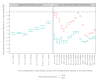
References
-
- Santé publique France (SPF). COVID-19 - Point épidémiologique hebdomadaire du 23 décembre 2021. [COVID-19 weekly epidemiological report of 23 December 2021]. Saint-Maurice: SPF. 23 Dec 2021. French. Available from: https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/content/download/400096/3305200
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Reinfection with SARS-CoV-2: implementation of a surveillance case definition within the EU/EEA. 8 April 2021. ECDC: Stockholm, 2021. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/reinfection-sars-cov-2-i...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
