Review and consensus recommendations on clinical APT-weighted imaging approaches at 3T: Application to brain tumors
- PMID: 35452155
- PMCID: PMC9321891
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.29241
Review and consensus recommendations on clinical APT-weighted imaging approaches at 3T: Application to brain tumors
Abstract
Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) MR imaging shows promise as a biomarker of brain tumor status. Currently used APTw MRI pulse sequences and protocols vary substantially among different institutes, and there are no agreed-on standards in the imaging community. Therefore, the results acquired from different research centers are difficult to compare, which hampers uniform clinical application and interpretation. This paper reviews current clinical APTw imaging approaches and provides a rationale for optimized APTw brain tumor imaging at 3 T, including specific recommendations for pulse sequences, acquisition protocols, and data processing methods. We expect that these consensus recommendations will become the first broadly accepted guidelines for APTw imaging of brain tumors on 3 T MRI systems from different vendors. This will allow more medical centers to use the same or comparable APTw MRI techniques for the detection, characterization, and monitoring of brain tumors, enabling multi-center trials in larger patient cohorts and, ultimately, routine clinical use.
Keywords: APT-weighted imaging; APTw standardization; CEST imaging; brain tumor.
© 2022 The Authors. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
J.Z. and P.C.M.v.Z. are paid lecturers for Philips and are the inventors of technology (including APTw MRI) licensed to Philips. P.C.M.v.Z. also has research support from Philips Healthcare. These arrangements have been approved by Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict‐of‐interest policies.
Figures
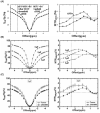
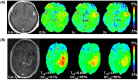
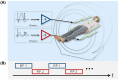
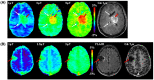




References
-
- Zhou J, Payen J, Wilson DA, Traystman RJ, van Zijl PCM. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nature Med. 2003;9:1085‐1090. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Lal B, Wilson DA, Laterra J, van Zijl PCM. Amide proton transfer (APT) contrast for imaging of brain tumors. Magn Reson Med. 2003;50:1120‐1126. - PubMed
-
- Ward KM, Aletras AH, Balaban RS. A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST). J Magn Reson. 2000;143:79‐87. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, van Zijl PC. Chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging and spectroscopy. Progr NMR Spectr. 2006;48:109‐136.

