Efficacy and speed of conversion of recent onset atrial fibrillation using oral propafenone versus parenteral amiodarone: A randomized controlled comparative study
- PMID: 35452688
- PMCID: PMC9243606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ihj.2022.04.006
Efficacy and speed of conversion of recent onset atrial fibrillation using oral propafenone versus parenteral amiodarone: A randomized controlled comparative study
Abstract
Background: Atrial fibrillation is the most commonly encountered arrhythmia. Several antiarrhythmic agents are effective in restoring and maintaining sinus rhythm.
Aim of the work: To compare the efficacy and rapidity of conversion of recent onset atrial fibrillation using oral propafenone versus intravenous infusion of amiodarone.
Methods: The study included 200 patients with recent onset atrial fibrillation. Patients were equally divided into 2 groups; group A where intravenous infusion amiodarone was given and group B where oral propafenone was administrated. The effectiveness and the time needed for conversion of atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm were compared in both groups.
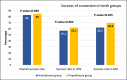
Results: The success of conversion of atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm was 83% in group A and 85% in group B, p-value = 0.699. The time elapsed from drug administration till conversion of atrial fibrillation was 9.07 ± 5.04 hours in group A versus 3.9 ± 1.54 hours in group B, p-value = 0.001. In both groups, patients who showed failed conversion had a significantly larger left atrial diameter and a significantly higher high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) level.
Conclusion: Oral propafenone was faster than parenteral amiodarone in the conversion of recent onset atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm. Patients with failed conversion had a bigger left atrial diameter and a higher hsCRP when compared to patients with successful conversion.
Keywords: Amiodarone; Atrial fibrillation; Propafenone.
Copyright © 2022 Cardiological Society of India. Published by Elsevier, a division of RELX India, Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Authors have nothing to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Balta S., Aparci M., Yildirim A.O., Demir M., Ozturk C., Celik T. The relation between flow mediated dilation and atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 2016;203:1157. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y.-Y., Qiu C., Davis P.J., et al. Predictors of progression of recently diagnosed atrial fibrillation in REgistry on cardiac rhythm DisORDers assessing the control of atrial fibrillation (RecordAF)-United States cohort. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(1):79–84. - PubMed
-
- Lüker J., Sultan A., Sehner S., et al. Use of antiarrhythmic drugs during ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: observations from a large single-centre cohort. Heart Ves. 2016;31(10):1669–1675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

