Dietary Iron Restriction Improves Muscle Function, Dyslipidemia, and Decreased Muscle Oxidative Stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 35453417
- PMCID: PMC9030937
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11040731
Dietary Iron Restriction Improves Muscle Function, Dyslipidemia, and Decreased Muscle Oxidative Stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Abstract
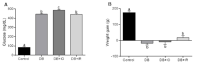
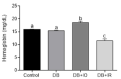
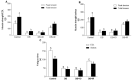
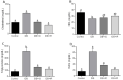
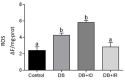
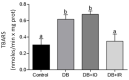
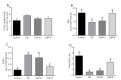
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic degenerative disease characterized by hyperglycemia and oxidative stress. Iron catalyzes free radical overproduction. High iron concentrations have previously been reported to promote an increase in oxidative stress; however, the effect of iron restriction in diabetes has not yet been explored, so we tested to see if iron restriction in diabetic rats reduces oxidative damage and improved muscle function. Wistar rats were assigned to 4 groups: Control; Diabetic; Diabetic rats with a high iron diet, and Diabetic with dietary iron restriction. After 8 weeks the rats were sacrificed, the muscles were extracted to prepare homogenates, and serum was obtained for biochemical measurements. Low iron diabetic rats showed an increase in the development of muscle strength in both muscles. Dietary iron restriction decreased triglyceride concentrations compared to the untreated diabetic rats and the levels of extremely low-density lipoproteins. Aggravation of lipid peroxidation was observed in the diabetic group with a high iron diet, while these levels remained low with iron restriction. Iron restriction improved muscle strength development and reduced fatigue times; this was related to better lipid profile control and decreased oxidant stress markers.
Keywords: diabetes; fatigue; iron; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diazoxide improves muscle function in association with improved dyslipidemia and decreased muscle oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2023 Feb;55(1):71-78. doi: 10.1007/s10863-023-09958-7. Epub 2023 Feb 1. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2023. PMID: 36723797
-
Effects of dietary iron restriction on kidney mitochondria function and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-diabetic rats.Mitochondrion. 2020 Sep;54:41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Mitochondrion. 2020. PMID: 32673787
-
Food restriction promotes damage reduction in rat models of type 2 diabetes mellitus.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 20;13(6):e0199479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199479. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29924854 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary restriction improves systemic and muscular oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats.J Physiol Biochem. 2011 Dec;67(4):613-9. doi: 10.1007/s13105-011-0108-0. Epub 2011 Jun 23. J Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21698418
-
Centaurium erythraea methanol extract protects red blood cells from oxidative damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Apr 18;202:172-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.03.016. Epub 2017 Mar 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28323046
Cited by
-
Relationship Between Whole Blood Iron Levels and Lipid Profile Parameters in the General Population: Findings from Routine Physical Examination Report.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Jul;203(7):3678-3684. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04459-z. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39630329
-
Serum ferritin associated with atherogenic lipid profiles in a high-altitude living general population.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 24;13:e19104. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19104. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40151449 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between serum iron level and physical function in heart failure patients is lost by presence of diabetes.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Feb;11(1):513-523. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14610. Epub 2023 Dec 13. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38088258 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

