Blockade on Lin28a Prevents Cognitive Impairment and Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier Induced by Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion
- PMID: 35453602
- PMCID: PMC9029709
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10040852
Blockade on Lin28a Prevents Cognitive Impairment and Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier Induced by Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion
Abstract
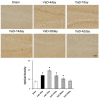
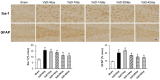
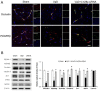
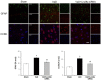
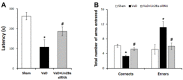
Lin28a is an RNA-binding protein involved in the translation and regulation of multiple mRNAs. Lin28a is overexpressed in animal models of brain injury. Similarly, our preliminary study found increased Lin28a expression levels in the animal models four to seven days after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Therefore, this current study aimed to evaluate the effects of modulating Lin28a on cognition and brain functions. Vascular dementia (VaD) was induced in 12-week-old male Wistar rats using permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO), and these rats were treated with Lin28a siRNA on the fourth and seventh day after BCCAO. From the 42nd day after BCCAO, cognitive behavioral experiments were performed for two weeks. VaD induced by BCCAO resulted in cognitive impairment and microglial activation. Lin28a expression was upregulated after BCCAO. Lin28a siRNA treatment alleviated cognitive impairment and overexpression of GFAP and Iba-1 in the brain. Furthermore, the treatment ameliorated the VaD-induced damage to the blood-brain barrier (BBB) components, including PECAM-1, PDGFRβ, occludin, claudin-9, and ZO-1. CCR6 activation after VaD, associated with BBB disruption, was diminished by treatment with Lin28a siRNA. The treatment inhibited VaD-induced microglial activity and alleviated BBB damage. Thus, blocking Lin28a may alleviate cognitive impairment caused by VaD.
Keywords: Lin28a; blood-brain barrier; chronic cerebral hypoperfusion; cognitive impairment; vascular dementia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

