A Small Molecule Promoting Neural Differentiation Suppresses Cancer Stem Cells in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 35453609
- PMCID: PMC9025482
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10040859
A Small Molecule Promoting Neural Differentiation Suppresses Cancer Stem Cells in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
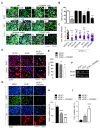
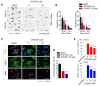
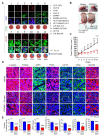
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a tumor cell subpopulation that drives tumor progression and metastasis, leading to a poor overall survival of patients. In colorectal cancer (CRC), the hyper-activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by a mutation of both adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) and K-Ras increases the size of the CSC population. We previously showed that CPD0857 inactivates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by promoting the ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of β-catenin and Ras proteins, thereby decreasing proliferation and increasing the apoptosis of CRC lines. CPD0857 also decreased the growth and invasiveness of CRC cells harboring mutant K-Ras resistant to EGFR mAb therapy. Here, we show that CPD0857 treatment decreases proliferation and increases the neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells (NPCs). CDP0857 effectively reduced the expression of CSC markers and suppressed self-renewal capacity. CPD0857 treatment also inhibited the proliferation and expression of CSC markers in D-K-Ras MT cells carrying K-Ras, APC and PI3K mutations, indicating the inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling. Moreover, CPD0857-treated xenograft mice showed a regression of tumor growth and decreased numbers of CSCs in tumors. We conclude that CPD0857 could serve as the basis of a drug development strategy targeting CSCs activated through Wnt/β-catenin-Ras MAPK-PI3K/AKT signaling in CRCs.
Keywords: K-Ras; Wnt/β-catenin; cancer stem cell; colorectal cancer; neural progenitor cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Merlos-Suarez A., Barriga F.M., Jung P., Iglesias M., Cespedes M.V., Rossell D., Sevillano M., Hernando-Momblona X., da Silva-Diz V., Muñoz P., et al. The intestinal stem cell signature identifies colorectal cancer stem cells and predicts disease relapse. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8:511–524. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.02.020. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

