Recombinant Klotho Protein Ameliorates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Attenuating Sterile Inflammation
- PMID: 35453645
- PMCID: PMC9032004
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10040894
Recombinant Klotho Protein Ameliorates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Attenuating Sterile Inflammation
Abstract
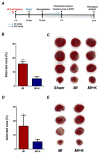
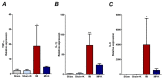
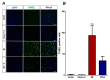
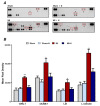
Currently, no effective therapy and potential target have been elucidated for preventing myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury (I/R). We hypothesized that the administration of recombinant klotho (rKL) protein could attenuate the sterile inflammation in peri-infarct regions by inhibiting the extracellular release of high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1). This hypothesis was examined using a rat coronary artery ligation model. Rats were divided into sham, sham+ rKL, I/R, and I/R+ rKL groups (n = 5/group). Administration of rKL protein reduced infarct volume and attenuated extracellular release of HMGB1 from peri-infarct tissue after myocardial I/R injury. The administration of rKL protein inhibited the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the peri-infarct regions and significantly attenuated apoptosis and production of intracellular reactive oxygen species by myocardial I/R injury. Klotho treatment significantly reduced the increase in the levels of circulating HMGB1 in blood at 4 h after myocardial ischemia. rKL regulated the levels of inflammation-related proteins. This is the first study to suggest that exogenous administration of rKL exerts myocardial protection effects after I/R injury and provides new mechanistic insights into rKL that can provide the theoretical basis for clinical application of new adjunctive modality for critical care of acute myocardial infarction.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; high mobility group box-1; klotho; myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; sterile inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Greulich S., Mayr A., Gloekler S., Seitz A., Birkmeier S., Schäufele T., Bekeredjian R., Zuern C.S., Seizer P., Geisler T., et al. Time-dependent myocardial necrosis in patients with st-segment-elevation myocardial infarction without angiographic collateral flow visualized by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging: Results from the multicenter stemi-scar project. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019;8:e012429. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012429. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kushner F.G., Hand M., Smith S.C., Jr., King S.B., 3rd, Anderson J.L., Antman E.M., Bailey S.R., Bates E.R., Blankenship J.C., Casey D.E., Jr., et al. 2009 focused updates: Acc/aha guidelines for the management of patients with st-elevation myocardial infarction (updating the 2004 guideline and 2007 focused update) and acc/aha/scai guidelines on percutaneous coronary intervention (updating the 2005 guideline and 2007 focused update): A report of the american college of cardiology foundation/american heart association task force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2009;120:2271–2306. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- NRF - 2019R1C1C1006332/National Research Foundation of Korea
- NRF- 2018R1C1B6006159/National Research Foundation of Korea
- NRF-2018R1D1A1B07044998/National Research Foundation of Korea
- NRF-2021R1C1C1009209/National Research Foundation of Korea
- 6-2020-0086/faculty research grant from Yonsei University College of Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

