An Imaging Overview of COVID-19 ARDS in ICU Patients and Its Complications: A Pictorial Review
- PMID: 35453894
- PMCID: PMC9032937
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12040846
An Imaging Overview of COVID-19 ARDS in ICU Patients and Its Complications: A Pictorial Review
Abstract
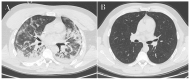
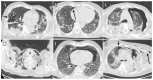
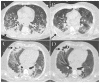
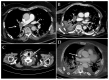
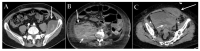
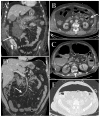
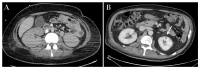
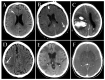
A significant proportion of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia could develop acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), thus requiring mechanical ventilation, and resulting in a high rate of intensive care unit (ICU) admission. Several complications can arise during an ICU stay, from both COVID-19 infection and the respiratory supporting system, including barotraumas (pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum), superimposed pneumonia, coagulation disorders (pulmonary embolism, venous thromboembolism, hemorrhages and acute ischemic stroke), abdominal involvement (acute mesenteric ischemia, pancreatitis and acute kidney injury) and sarcopenia. Imaging plays a pivotal role in the detection and monitoring of ICU complications and is expanding even to prognosis prediction. The present pictorial review describes the clinicopathological and radiological findings of COVID-19 ARDS in ICU patients and discusses the imaging features of complications related to invasive ventilation support, as well as those of COVID-19 itself in this particularly fragile population. Radiologists need to be familiar with COVID-19's possible extra-pulmonary complications and, through reliable and constant monitoring, guide therapeutic decisions. Moreover, as more research is pursued and the pathophysiology of COVID-19 is increasingly understood, the role of imaging must evolve accordingly, expanding from the diagnosis and subsequent management of patients to prognosis prediction.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; intensive care; lung CT; mechanical intubation; pneumomediastinum; pneumothorax; pulmonary embolism; superinfection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
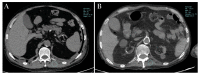
References
-
- Simpson S., Kay F.U., Abbara S., Bhalla S., Chung J.H., Chung M., Henry T.S., Kanne J.P., Kligerman S., Ko J.P., et al. Radiological Society of North America Expert Consensus Statement on Reporting Chest CT Findings Related to COVID-19. Endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Radiology, the American College of Radiology, and RSNA—Secondary Publication. J. Thorac. Imaging. 2020;35:219–227. doi: 10.1097/RTI.0000000000000524. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balacchi C., Brandi N., Ciccarese F., Coppola F., Lucidi V., Bartalena L., Parmeggiani A., Paccapelo A., Golfieri R. Comparing the first and the second waves of COVID-19 in Italy: Differences in epidemiological features and CT findings using a semi-quantitative score. Emerg. Radiol. 2021;28:1055–1067. doi: 10.1007/s10140-021-01937-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ciccarese F., Coppola F., Spinelli D., Galletta G.L., Lucidi V., Paccapelo A., DE Benedittis C., Balacchi C., Golfieri R. Diagnostic Accuracy of North America Expert Consensus Statement on Reporting CT Findings in Patients Suspected of Having COVID-19 Infection: An Italian Single-Center Experience. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging. 2020;2:e200312. doi: 10.1148/ryct.2020200312. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angeli E., Dalto S., Marchese S., Setti L., Bonacina M., Galli F., Rulli E., Torri V., Monti C., Meroni R., et al. Prognostic value of CT integrated with clinical and laboratory data during the first peak of the COVID-19 pandemic in Northern Italy: A nomogram to predict unfavorable outcome. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021;137:109612. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.109612. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

