Nucleic Acid Biomarkers in Waldenström Macroglobulinemia and IgM-MGUS: Current Insights and Clinical Relevance
- PMID: 35454017
- PMCID: PMC9028641
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12040969
Nucleic Acid Biomarkers in Waldenström Macroglobulinemia and IgM-MGUS: Current Insights and Clinical Relevance
Abstract
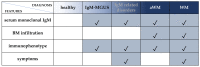
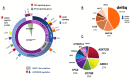
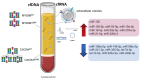
Waldenström Macroglobulinemia (WM) is an indolent lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, characterized by the production of excess immunoglobulin M monoclonal protein. WM belongs to the spectrum of IgM gammopathies, ranging from asymptomatic IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (IgM-MGUS), through IgM-related disorders and asymptomatic WM to symptomatic WM. In recent years, its complex genomic and transcriptomic landscape has been extensively explored, hereby elucidating the biological mechanisms underlying disease onset, progression and therapy response. An increasing number of mutations, cytogenetic abnormalities, and molecular signatures have been described that have diagnostic, phenotype defining or prognostic implications. Moreover, cell-free nucleic acid biomarkers are increasingly being investigated, benefiting the patient in a minimally invasive way. This review aims to provide an extensive overview of molecular biomarkers in WM and IgM-MGUS, considering current shortcomings, as well as potential future applications in a precision medicine approach.
Keywords: CXCR4; IgM-MGUS; MYD88; WM; cfDNA; liquid biopsy; lncRNA; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Remstein E.D., Hanson C.A., Kyle R.A., Hodnefield J.M., Kurtin P.J. Despite apparent morphologic and immunophenotypic heterogeneity, Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia is consistently composed of cells along a morphologic continuum of small lymphocytes, plasmacytoid lymphocytes, and plasma cells. Semin. Oncol. 2003;30:182–186. doi: 10.1053/sonc.2003.50073. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

