Cannabis Biomolecule Effects on Cancer Cells and Cancer Stem Cells: Cytotoxic, Anti-Proliferative, and Anti-Migratory Activities
- PMID: 35454080
- PMCID: PMC9028333
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12040491
Cannabis Biomolecule Effects on Cancer Cells and Cancer Stem Cells: Cytotoxic, Anti-Proliferative, and Anti-Migratory Activities
Abstract
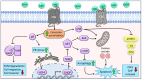
Cancer is a complex family of diseases affecting millions of people worldwide. Gliomas are primary brain tumors that account for ~80% of all malignant brain tumors. Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common, invasive, and lethal subtype of glioma. Therapy resistance and intra-GBM tumoral heterogeneity are promoted by subpopulations of glioma stem cells (GSCs). Cannabis sativa produces hundreds of secondary metabolites, such as flavonoids, terpenes, and phytocannabinoids. Around 160 phytocannabinoids have been identified in C. sativa. Cannabis is commonly used to treat various medical conditions, and it is used in the palliative care of cancer patients. The anti-cancer properties of cannabis compounds include cytotoxic, anti-proliferative, and anti-migratory activities on cancer cells and cancer stem cells. The endocannabinoids system is widely distributed in the body, and its dysregulation is associated with different diseases, including various types of cancer. Anti-cancer activities of phytocannabinoids are mediated in glioma cells, at least partially, by the endocannabinoid receptors, triggering various cellular signaling pathways, including the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress pathway. Specific combinations of multiple phytocannabinoids act synergistically against cancer cells and may trigger different anti-cancer signaling pathways. Yet, due to scarcity of clinical trials, there remains no solid basis for the anti-cancer therapeutic potential of cannabis compounds.
Keywords: cancer; cancer stem cells; cannabinoid receptors; cannabis; cytotoxicity; glioblastoma; glioma; phytocannabinoids; synergy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ruddon R.W. Cancer Biology. Oxford University Press; New York, NY, USA: 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

