Elevated Gamma Connectivity in Nidopallium Caudolaterale of Pigeons during Spatial Path Adjustment
- PMID: 35454265
- PMCID: PMC9026408
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12081019
Elevated Gamma Connectivity in Nidopallium Caudolaterale of Pigeons during Spatial Path Adjustment
Abstract
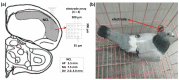
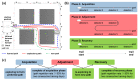
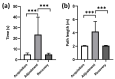
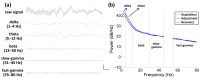
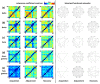
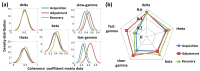
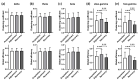
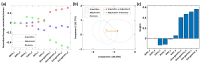
Previous studies showed that spatial navigation depends on a local network including multiple brain regions with strong interactions. However, it is still not fully understood whether and how the neural patterns in avian nidopallium caudolaterale (NCL), which is suggested to play a key role in navigation as a higher cognitive structure, are modulated by the behaviors during spatial navigation, especially involved path adjustment needs. Hence, we examined neural activity in the NCL of pigeons and explored the local field potentials' (LFPs) spectral and functional connectivity patterns in a goal-directed spatial cognitive task with the detour paradigm. We found the pigeons progressively learned to solve the path adjustment task when the learned path was blocked suddenly. Importantly, the behavioral changes during the adjustment were accompanied by the modifications in neural patterns in the NCL. Specifically, the spectral power in lower bands (1-4 Hz and 5-12 Hz) decreased as the pigeons were tested during the adjustment. Meanwhile, an elevated gamma (31-45 Hz and 55-80 Hz) connectivity in the NCL was also detected. These results and the partial least square discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) modeling analysis provide insights into the neural activities in the avian NCL during the spatial path adjustment, contributing to understanding the potential mechanism of avian spatial encoding. This study suggests the important role of the NCL in spatial learning, especially path adjustment in avian navigation.
Keywords: functional connectivity; gamma; nidopallium caudolaterale; path adjustment; pigeon; spatial navigation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced Hippocampus-Nidopallium Caudolaterale Connectivity during Route Formation in Goal-Directed Spatial Learning of Pigeons.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jul 5;11(7):2003. doi: 10.3390/ani11072003. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359131 Free PMC article.
-
Disarrangement and reorganization of the hippocampal functional connectivity during the spatial path adjustment of pigeons.BMC Zool. 2022 Oct 4;7(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s40850-022-00143-8. BMC Zool. 2022. PMID: 37170160 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Hippocampus-Nidopallium Caudolaterale Interaction in Visual-Spatial Associative Learning of Pigeons.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jan 30;14(3):456. doi: 10.3390/ani14030456. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38338099 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Hp-NCL Network in Goal-Directed Routing Information Encoding of Bird: A Review.Brain Sci. 2020 Sep 7;10(9):617. doi: 10.3390/brainsci10090617. Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 32906650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural Substrates of Homing Pigeon Spatial Navigation: Results From Electrophysiology Studies.Front Psychol. 2022 Apr 6;13:867939. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.867939. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35465504 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-Frequency Local Field Potential Oscillations for Pigeons in Effective Turning.Animals (Basel). 2024 Feb 3;14(3):509. doi: 10.3390/ani14030509. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38338152 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-Amplitude Coupling between Theta Rhythm and High-Frequency Oscillations in the Hippocampus of Pigeons during Navigation.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jan 29;14(3):439. doi: 10.3390/ani14030439. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38338082 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-band-based dynamic functional connectivity in pigeon entopallium during sample presentation in a delayed color matching task.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Feb;18(1):37-47. doi: 10.1007/s11571-022-09916-w. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 38406198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poucet B., Thinus-Blanc C., Chapuis N. Route planning in cats, in relation to the visibility of the goal. Anim. Behav. 1983;31:594–599. doi: 10.1016/S0003-3472(83)80083-9. - DOI
-
- Negrón-Oyarzo I., Espinosa N., Aguilar-Rivera M., Fuenzalida M., Aboitiz F., Fuentealba P. Coordinated prefrontal–hippocampal activity and navigation strategy-related prefrontal firing during spatial memory formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:7123–7128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720117115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

