Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Mitochondrial Reprogramming in Cancer
- PMID: 35454774
- PMCID: PMC9032679
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14081865
Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Mitochondrial Reprogramming in Cancer
Abstract
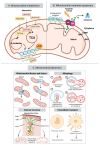
Altered metabolism is a defining hallmark of cancer. Metabolic adaptations are often linked to a reprogramming of the mitochondria due to the importance of these organelles in energy production and biosynthesis. Cancer cells present heterogeneous metabolic phenotypes that can be modulated by signals originating from the tumor microenvironment. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are recognized as key players in intercellular communications and mediate many of the hallmarks of cancer via the delivery of their diverse biological cargo molecules. Firstly, this review introduces the most characteristic changes that the EV-biogenesis machinery and mitochondria undergo in the context of cancer. Then, it focuses on the EV-driven processes which alter mitochondrial structure, composition, and function to provide a survival advantage to cancer cells in the context of the hallmarks of cancers, such as altered metabolic strategies, migration and invasiveness, immune surveillance escape, and evasion of apoptosis. Finally, it explores the as yet untapped potential of targeting mitochondria using EVs as delivery vectors as a promising cancer therapeutic strategy.
Keywords: metabolism; miRNA; mitochondrial dynamics; tumor microenvironment (TME); tumor-derived EVs (TEVs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Théry C., Witwer K.W., Aikawa E., Alcaraz M.J., Anderson J.D., Andriantsitohaina R., Antoniou A., Arab T., Archer F., Atkin-Smith G.K., et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2018;7:1535750. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

