Aspirin-Triggered Resolvin D1 Reduces Chronic Dust-Induced Lung Pathology without Altering Susceptibility to Dust-Enhanced Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 35454807
- PMCID: PMC9032113
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14081900
Aspirin-Triggered Resolvin D1 Reduces Chronic Dust-Induced Lung Pathology without Altering Susceptibility to Dust-Enhanced Carcinogenesis
Abstract
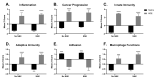
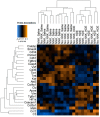
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with increased risk being associated with unresolved or chronic inflammation. Agricultural and livestock workers endure significant exposure to agricultural dusts on a routine basis; however, the chronic inflammatory and carcinogenic effects of these dust exposure is unclear. We have developed a chronic dust exposure model of lung carcinogenesis in which mice were intranasally challenged three times a week for 24 weeks, using an aqueous dust extract (HDE) made from dust collected in swine confinement facilities. We also treated mice with the omega-3-fatty acid lipid mediator, aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 (AT-RvD1) to provide a novel therapeutic strategy for mitigating the inflammatory and carcinogenic effects of HDE. Exposure to HDE resulted in significant immune cell influx into the lungs, enhanced lung tumorigenesis, severe tissue pathogenesis, and a pro-inflammatory and carcinogenic gene signature, relative to saline-exposed mice. AT-RvD1 treatment mitigated the dust-induced inflammatory response but did not protect against HDE + NNK-enhanced tumorigenesis. Our data suggest that chronic HDE exposure induces a significant inflammatory and pro-carcinogenic response, whereas treatment with AT-RvD1 dampens the inflammatory responses, providing a strong argument for the therapeutic use of AT-RvD1 to mitigate chronic inflammation.
Keywords: epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT); fibrosis; lung cancer; lung inflammation; omega-3 fatty acids; organic dust; specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPM); therapeutic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Romberger D.J., Heires A.J., Nordgren T.M., Souder C.P., West W., Liu X.-d., Poole J.A., Toews M.L., Wyatt T.A. Proteases in agricultural dust induce lung inflammation through PAR-1 and PAR-2 activation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2015;309:L388–L399. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00025.2015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

