Where Do We Stand in the Management of Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer? A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 35454924
- PMCID: PMC9029666
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14082017
Where Do We Stand in the Management of Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer? A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
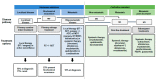
Oligometastatic prostate cancer (OMPC) is an intermediate state between localised disease and widespread metastases that includes a spectrum of disease biology and clinical behaviours. This narrative review will cover the current OMPC scenario. We conducted comprehensive English language literature research for original and review articles using the Medline database and grey literature through December 2021. OMPC is a unique clinical state with inherently more indolent tumour biology susceptible to multidisciplinary treatment (MDT). With the development of new imaging techniques, patients with OMPC are likely to be identified at an earlier stage, and the paradigm for treatment is shifting towards a more aggressive approach to treating potentially curable patients. Multimodal management is necessary to improve patient outcomes due to the combination of available therapies, such as local therapy of primary tumour, metastasis directed therapy or systemic therapy, to reduce tumour load and prevent further disease progression. Additional prospective data are needed to select patients most likely to benefit from a given therapeutic approach.
Keywords: local therapy; metastasis-directed treatment; new imaging techniques; oligometastatic; prostate cancer; systemic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
G.R.J. has received advisory board: Janssen, Bayer, MSD, honoraria for lectures/travel expenses: Janssen, Astellas, Recordati and research funding: Fundación para la Investigación en Urología (FIU). P.V.J. has received honoraria for speaker engagements, advisory roles or continuous medical education: Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Janssen, MSD, Bayer, Pfizer, Eisai, Ipsen, Sanofi, Roche, BMS, Merck, research funding: Astellas, Pfizer and consultant: Astellas, Roche. V.C.N. has received honoraria for speaker: Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Astellas, Janssen, Roche, MSD, Ipsen and honoraria for travel: Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, BMS. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gillessen S., Omlin A., Attard G., de Bono J.S., Efstathiou E., Fizazi K., Halabi S., Nelson P.S., Sartor O., Smith M.R., et al. Management of patients with advanced prostate cancer: Recommendations of the St Gallen Advanced Prostate Cancer Consensus Conference (APCCC) 2015. Ann. Oncol. 2015;26:1589–1604. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv257. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

