A Bioinformatics Evaluation of the Role of Dual-Specificity Tyrosine-Regulated Kinases in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 35454940
- PMCID: PMC9025863
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14082034
A Bioinformatics Evaluation of the Role of Dual-Specificity Tyrosine-Regulated Kinases in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
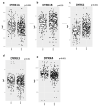
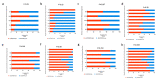
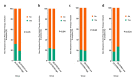
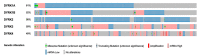
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer worldwide and has an increasing incidence in younger populations. The dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinase (DYRK) family has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer. However, the role and contribution of the distinct family members in regulating CRC tumorigenesis has not been addressed yet. Herein, we used publicly available CRC patient datasets (TCGA RNA sequence) and several bioinformatics webtools to perform in silico analysis (GTEx, GENT2, GEPIA2, cBioPortal, GSCALite, TIMER2, and UALCAN). We aimed to investigate the DYRK family member expression pattern, prognostic value, and oncological roles in CRC. This study shed light on the role of distinct DYRK family members in CRC and their potential outcome predictive value. Based on mRNA level, DYRK1A is upregulated in late tumor stages, with lymph node and distant metastasis. All DYRKs were found to be implicated in cancer-associated pathways, indicating their key role in CRC pathogenesis. No significant DYRK mutations were identified, suggesting that DYRK expression variation in normal vs. tumor samples is likely linked to epigenetic regulation. The expression of DYRK1A and DYRK3 expression correlated with immune-infiltrating cells in the tumor microenvironment and was upregulated in MSI subtypes, pointing to their potential role as biomarkers for immunotherapy. This comprehensive bioinformatics analysis will set directions for future biological studies to further exploit the molecular basis of these findings and explore the potential of DYRK1A modulation as a novel targeted therapy for CRC.
Keywords: DYRK1A; bioinformatics; colorectal cancer; dual-specificity tyrosine-regulated kinases (DYRKs); kinases; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Zacharakis M., Xynos I.D., Lazaris A., Smaro T., Kosmas C., Dokou A., Felekouras E., Antoniou E., Polyzos A., Sarantonis J., et al. Predictors of survival in stage IV metastatic colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:653–660. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

