Self-Assembled Nanomicellar Formulation of Docetaxel as a Potential Breast Cancer Chemotherapeutic System
- PMID: 35454976
- PMCID: PMC9024535
- DOI: 10.3390/life12040485
Self-Assembled Nanomicellar Formulation of Docetaxel as a Potential Breast Cancer Chemotherapeutic System
Abstract
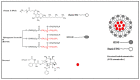
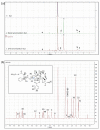
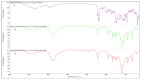
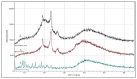
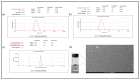
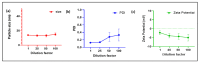
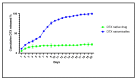
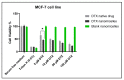
Docetaxel (DTX) is classified as a class IV drug that exhibits poor aqueous solubility (6-7 µg/mL in water) and permeability (P-glycoprotein substrate). The main objective of this study was to construct, characterize, and evaluate docetaxel loaded nanomicellar formulation in vitro for oral delivery to enhance the absorption and bioavailability of DTX, as well as to circumvent P-gp efflux inhibition. Formulations were prepared with two polymeric surfactants, hydrogenated castor oil-40 (HCO-40) and D-α-Tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (VIT E TPGS) with solvent evaporation technique, and the resulting DTX nanomicellar formulations were characterized by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Proton NMR, FT-IR, and XRD data indicated that DTX was completely encapsulated within the hydrophobic core of the nanomicelles in its amorphous state. TEM data revealed a smooth spherical shape of the nanomicellar formulation. The optimized formulation (F-2) possessed a mean diameter of 13.42 nm, a zeta potential of -0.19 mV, with a 99.3% entrapment efficiency. Dilution stability study indicated that nanomicelles were stable up to 100-fold dilution with minimal change in size, poly dispersity index (PDI), and zeta potential. In vitro cytotoxicity study revealed higher anticancer activity of DTX nanomicelles at 5 µM compared to the native drug against breast cancer cell line (MCF-7) cells. The LC-MS data confirmed the chemical stability of DTX within the nanomicelles. In vitro drug release study demonstrated faster dissolution of DTX from the nanomicelles compared to the naked drug. Our experimental results exhibit that nanomicelles could be a drug delivery system of choice to encapsulate drugs with low aqueous solubility and permeability that can preserve the stability of the active constituents to provide anticancer activity.
Keywords: anticancer activity; breast cancer; docetaxel; enhanced solubility; nanomicelles; vitamin E TPGS delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Xiang L., Song Z., Rong G. Taxotere-induced WNT16 Expression in Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts Might Associate with Progression and Chemoresistance of Breast Cancer. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020;50:205–212. - PubMed
-
- Babasaki T., Sentani K., Sekino Y., Kobayashi G., Thang Pham Q., Katsuya N., Akabane S., Taniyama D., Hayashi T., Shiota M., et al. Overexpression of claspin promotes docetaxel resistance and is associated with prostate-specific antigen recurrence in prostate cancer. Cancer Med. 2021;10:5574–5588. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

