A Third Dose of the COVID-19 Vaccine, CVnCoV, Increased the Neutralizing Activity against the SARS-CoV-2 Wild-Type and Delta Variant
- PMID: 35455257
- PMCID: PMC9025705
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10040508
A Third Dose of the COVID-19 Vaccine, CVnCoV, Increased the Neutralizing Activity against the SARS-CoV-2 Wild-Type and Delta Variant
Abstract
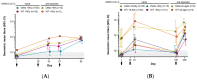
A third dose of CVnCoV, a former candidate mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, was previously shown to boost neutralizing antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 wild-type in adults aged 18−60 and >60 years in a phase 2a clinical study. In the present study, we report the neutralizing antibody responses to a wild-type and a variant of concern, Delta, after a third dose of the vaccine on day (D)57 and D180. Neutralization activity was assessed using a microneutralization assay. Comparable levels of neutralizing antibodies against the wild-type and Delta were induced. These were higher than those observed after the first two doses, irrespective of age or pre-SARS-CoV-2-exposure status, indicating that the first two doses induced immune memory. Four weeks after the third dose on D180, the neutralizing titers for wild-type and Delta were two-fold higher in younger participants than in older participants; seroconversion rates were 100% for wild-type and Delta in the younger group and for Delta in the older group. A third CVnCoV dose induced similar levels of neutralizing responses against wild-type virus and the Delta variant in both naïve and pre-exposed participants, aligning with current knowledge from licensed COVID-19 vaccines that a third dose is beneficial against SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; SARS-CoV-2; delta variant; neutralizing antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employed by CureVac and hold company shares/stock options as part of their remuneration package.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. [(accessed on 2 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/
-
- WHO. [(accessed on 2 February 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Wibmer C.K., Ayres F., Hermanus T., Madzivhandila M., Kgagudi P., Oosthuysen B., Lambson B.E., de Oliveira T., Vermeulen M., van der Berg K., et al. SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 escapes neutralization by South African COVID-19 donor plasma. Nat. Med. 2021;27:622–625. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01285-x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

