Parental COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy for Children in Romania: National Survey
- PMID: 35455296
- PMCID: PMC9024740
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10040547
Parental COVID-19 Vaccine Hesitancy for Children in Romania: National Survey
Abstract
Purpose: Once vaccination against COVID-19 was also possible for children over 12 years of age, parents/legal guardians had to give their consent for their vaccination. It is a crucial moment, given the large number of infected people in Romania and the fact that these children are a source of transmission of the virus in the community. The refusal or hesitation of the parents/legal guardians, regarding the agreement for the vaccination of the children, determined us to focus on this subject, wishing, based on the questioning of as many parents as possible, to extract the reasons underlying these decisions.
Methods: This study is designed to observe the attitudes of parents/legal guardians regarding the refusal, hesitation, or acceptance of vaccination of children. The persons targeted to answer the questionnaire had to meet three conditions: to be at least 21 years old, to have a stable residence in Romania, and to be parents/legal guardians of at least one child under 18 years of age. The questionnaire was applied online to a number of 581 parents/legal guardians, being structured to obtain socio-demographic data and other categories of data that allow us to analyze their views on vaccinating children.
Results: Sociological data resulting from the application of the questionnaire on 581 parents/legal guardians show that 183 (31.5%) adults and 140 (24.1%) children got infected with COVID-19. The total number of respondents shows that only 411 (70.7%) adults and 185 (31.8%) children are vaccinated.
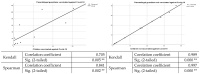
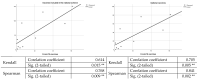
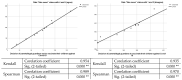
Conclusions: From the analysis of the data obtained through the questionnaire, following the application of the Kendall and Spearman statistical analysis tests, it is found that there is a strong link between participants' trust/distrust in "fake news" information and their decision to vaccinate their children.
Keywords: Romania; anti-COVID-19 vaccine; children vaccination; hesitation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Survey upon the Reasons of COVID-19 Vaccination Acceptance in Romania.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 8;10(10):1679. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10101679. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36298544 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Vaccine Perspective From Adolescents' Lens in the US.Cureus. 2024 Feb 4;16(2):e53566. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53566. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38445148 Free PMC article.
-
Parents'Attitudes, Their Acceptance of the COVID-19 Vaccines for Children and the Contributing Factors in Najran, Saudi Arabia: A Cross-Sectional Survey.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Aug 6;10(8):1264. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10081264. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36016152 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Factors influencing parents' decisions to vaccinate children against COVID-19.Vaccine. 2023 Oct 13;41(43):6419-6425. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.09.020. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Vaccine. 2023. PMID: 37735055 Review.
-
Worldwide Estimation of Parental Acceptance of COVID-19 Vaccine for Their Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Feb 24;11(3):533. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11030533. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36992117 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Survey upon the Reasons of COVID-19 Vaccination Acceptance in Romania.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 8;10(10):1679. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10101679. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36298544 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Vaccination of the Population of Romania against Monkeypox in Terms of Medical Security.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 29;10(11):1834. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111834. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366343 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis regarding the impact of 'fake news' on the quality of life of the population in a region affected by earthquake activity. The case of Romania-Northern Oltenia.Front Public Health. 2023 Dec 1;11:1244564. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1244564. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38106906 Free PMC article.
-
Has COVID-19 Modified the Weight of Known Systemic Inflammation Indexes and the New Ones (MCVL and IIC) in the Assessment as Predictive Factors of Complications and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis?Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 10;12(12):3118. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12123118. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553125 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis: A Propensity Score Matched Study Comparing before and during the Pandemic.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 22;13(14):2446. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13142446. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coronavirus Cases in the World. [(accessed on 10 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- Coronavirus Cases in Romania. [(accessed on 10 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/romania/
-
- Official data from Romania. [(accessed on 10 November 2021)]. Available online: https://datelazi.ro/
-
- COVID-19 Projections for Romania. [(accessed on 10 November 2021)]. Available online: https://covid19.healthdata.org/romania?view=daily-deaths&tab=trend.
-
- Romania, Bulgaria Hit Pandemic Death Highs Amid Vaccines Lag. [(accessed on 10 November 2021)]. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/romania-hits-pandemic-death-record-....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

