Daphne jejudoensis Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammation by Inhibiting TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, iNOS, and COX-2 Expression in Periodontal Ligament Cells
- PMID: 35455384
- PMCID: PMC9032301
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15040387
Daphne jejudoensis Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammation by Inhibiting TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, iNOS, and COX-2 Expression in Periodontal Ligament Cells
Abstract
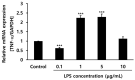
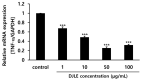
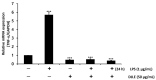
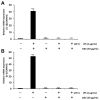
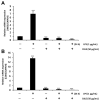
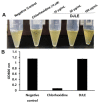
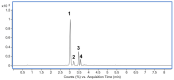
Periodontitis is a common disease involving inflammation and tissue destruction in the periodontal region. Although uncontrolled long-term inflammation in the gingiva may lead to loss of the periodontal ligament, treatments or preventive solutions for periodontitis are scarce. The aim of this study is to find anti-inflammatory material from a natural source that can be used to treat or protect against periodontitis. Daphne species (Thymelaeaceae) are important and popular components of traditional Chinese medicine and are used as anti-inflammatory agents. Daphne jejudoensis is an endemic plant that grows on Jeju Island and was identified as a new species in 2013. In this study, for the first time, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effect of D. jejudoensis leaf extract (DJLE) on human periodontal ligament cells. The gene expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1β and 6 and tumor necrosis factor-α) and inflammation-inducible enzymes (inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2) were reduced after DJLE treatment with/without lipopolysaccharide stimulation. The findings of this study indicate that D. jejudoensis possesses anti-inflammatory activities, suggesting that DJLE may be a potential preventive and therapeutic agent for periodontitis.
Keywords: Daphne jejudoensis; Thymelaeaceae; anti-inflammatory activity; lipopolysaccharide; periodontitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of apigenin on nicotine- and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human periodontal ligament cells via heme oxygenase-1.Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 Nov;9(12):1374-80. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2009.08.015. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19729077
-
Periodontal Disease as a Risk Factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-12. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-288. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820156
-
Biomolecular evidence of anti-inflammatory effects by Clematis mandshurica Ruprecht root extract in rodent cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1141-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.06.048. Epub 2014 Jun 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24975194
-
The anti-inflammatory role of heme oxygenase-1 in lipopolysaccharide and cytokine-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide production in human periodontal ligament cells.J Periodontol. 2009 Dec;80(12):2045-55. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090145. J Periodontol. 2009. PMID: 19961388
-
The Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib Inhibits Inflammatory Response of Periodontal Ligament Cells and Ameliorates Experimental Periodontitis in Rats.J Periodontol. 2017 May;88(5):473-483. doi: 10.1902/jop.2016.160396. Epub 2016 Dec 16. J Periodontol. 2017. PMID: 27982724
Cited by
-
Exploring the Potential of Micro-Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Periodontitis.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;14(5):552. doi: 10.3390/life14050552. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38792574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of NO Production in LPS-Stimulated Primary Rat Glial Cells by Gnidilatimonoein and Extract of Daphne mucronata.Iran J Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 1;21(2):e3052. doi: 10.30498/ijb.2023.285965.3052. eCollection 2023 Apr. Iran J Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37228631 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropharmacological potential of honokiol and its derivatives from Chinese herb Magnolia species: understandings from therapeutic viewpoint.Chin Med. 2023 Nov 24;18(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00846-1. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 38001538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects and related mechanisms of naringenin in human periodontal ligament stem cells under lipopolysaccharide stimulation based on RNA sequencing.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Aug 1;42(4):512-520. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2024.2023453. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39049640 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
DLK1 regulates periodontal inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB p65 and JNK signaling pathways.Odontology. 2025 Jan;113(1):349-357. doi: 10.1007/s10266-024-00979-1. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Odontology. 2025. PMID: 38995322
References
-
- Meng X., Zhang X., Su X., Liu X., Ren K., Ning C., Zhang Q., Zhang S. Daphnes Cortex and its licorice-processed products suppress inflammation via the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway and regulation of the metabolic profile in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022;283:114657. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114657. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

