Effects of Occupational Therapy via Telerehabilitation on Occupational Balance, Well-Being, Intrinsic Motivation and Quality of Life in Syrian Refugee Children in COVID-19 Lockdown: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35455529
- PMCID: PMC9026389
- DOI: 10.3390/children9040485
Effects of Occupational Therapy via Telerehabilitation on Occupational Balance, Well-Being, Intrinsic Motivation and Quality of Life in Syrian Refugee Children in COVID-19 Lockdown: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
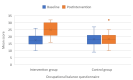
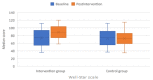
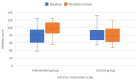
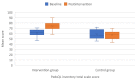
We aimed to evaluate the effects of an occupational training program via telerehabilitation on well-being (WB), occupational balance (OB), intrinsic motivation (IM), and quality of life (QoL) in Syrian refugee children resettled in Turkey during the COVID-19 pandemic. This was a single-center, prospective, randomized, non-blinded trial in which children aged 13-15 years and attending a secondary school were recruited. OB, WB, IM, and QoL were evaluated via the OB Questionnaire (OBQ11), the Well-Star Scale (WSS), the IM Scale (IMS), and the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL). The intervention group attended online occupational therapy classes. Online classes were carried out as five sessions per week, each session lasting 1 h, for 3 weeks. Questionnaires were performed at the outset of the study and following the training program. Overall, 52 refugee children were randomized into the intervention and control groups, each including 26 children. The mean OBQ11, WSS, IMS, and PedsQL scores significantly improved more in the intervention group than in the control group. This was the first study investigating the effects of a customized online training course on OB, WB, IM, and QoL in Syrian refugee children, also affected unfavorably by the COVID-19 lockdown. Our results showed significant improvements in all the study scales that we used to quantify the alterations in the aforementioned traits.
Keywords: COVID-19; children; occupational balance; occupational therapy; quality of life; refugee; well-being.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- UNICEF Press Release 11 March 2021. [(accessed on 2 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/press-releases/syria-conflict-10-years-90-cent-ch....
-
- Data from DGMM. [(accessed on 9 December 2021)]; Available online: https://en.sg.gov.tr/irregular-migration-statistics.
-
- UNICEF Turkey Humanitarian Situation Report No. 40, Reporting Period: January—December 2020. UNICEF Turkey. [(accessed on 23 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.unicef.org/turkey/en.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

