Impact of the Cognitive-Behavioral Approach and Psychoeducational Intervention in Breast Cancer Management: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 35455807
- PMCID: PMC9025943
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10040629
Impact of the Cognitive-Behavioral Approach and Psychoeducational Intervention in Breast Cancer Management: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
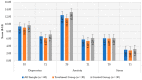
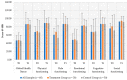
(1) Background: Breast cancer (BC) is the most prevalent malignancy in women. High cancer-related psychological distress levels have been observed in BC patients, with a potentially relevant impact on disease management, compliance with disease treatments, and everyday life activities and relationships. This work evaluated the effectiveness of three individual cognitive−behavioral therapy psychoeducational sessions versus a self-managed informative guide with individual counseling sessions without specific psychological treatment. (2) Methods: the intervention group received three individual 50-min sessions of psychoeducational training, and the control group received a self-managed informative guide with individual counseling sessions without any kind of psychological treatment. The Hospital Anxiety Depression Scale (HADS), the Distress Thermometer (DT), and the EORTC (European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer) QLQ-C30 were administered at baseline and two months after study inclusion. (3) Results: A total of 60 participants were included in the study (intervention group: 30, control group: 30). Significant improvements were observed in both groups after two months (p < 0.05), but no statistically significant differences emerged between groups. (4) Conclusions: Psychoeducational interventions and CBT help BC patients manage disease-related fear and distress, allowing them to achieve a good quality of life.
Keywords: RCT; breast cancer; cognitive behavioral approach; psychoeducational intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of psychoeducational interventions on sexual functioning, quality of life and psychological outcomes in patients with gynaecological cancer: A systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(58):4077-4164. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-406. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820522
-
Erratum.Mult Scler. 2016 Oct;22(12):NP9-NP11. doi: 10.1177/1352458515585718. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26041800
-
The effectiveness of a nurse-led intervention with the distress thermometer for patients treated with curative intent for breast cancer: design of a randomized controlled trial.BMC Cancer. 2016 Jul 25;16:520. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2565-x. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27455960 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions to improve self-management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Jun;24(28):1-232. doi: 10.3310/hta24280. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32568666 Free PMC article.
-
Telephone interventions for symptom management in adults with cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jun 2;6(6):CD007568. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007568.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32483832 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Related Factors with Depression and Anxiety in Mastectomized Women Breast Cancer Survivors.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 7;20(4):2881. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20042881. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36833577 Free PMC article.
-
Using temperament and character dimensions (TCI) to analyze the personality profiles of adults and older adults with cancer managed in outpatient settings.Front Psychol. 2024 Jan 15;14:1289093. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1289093. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38288360 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CBT-based interventions on health outcomes in breast cancer patients: a systematic review and Meta-analysis.Breast Cancer. 2025 Jul;32(4):689-704. doi: 10.1007/s12282-025-01711-9. Epub 2025 May 14. Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40366566
-
Application Value of Music Therapy in Improving the Emotional State and Quality of Life of Hospitalized Patients with Breast Cancer: Retrospective Study.Noise Health. 2024 Jul-Sep 01;26(122):357-362. doi: 10.4103/nah.nah_50_24. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Noise Health. 2024. PMID: 39345077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breastcancer.org U.S. Breast Cancer Statistics. [(accessed on 25 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.breastcancer.org/symptoms/understand_bc/statistics.
-
- Union E. Breast Cancer Burden in EU-27. [(accessed on 30 January 2022)]. Available online: https://ecis.jrc.ec.europa.eu/pdf/Breast_cancer_factsheet-Oct_2020.pdf.
-
- OECD Health at a Glance 2019—OECD Indicators. [(accessed on 30 January 2022)]. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/health/health-at-a-glance.htm.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources