Stem-Cell Therapy for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) in Newborns
- PMID: 35455954
- PMCID: PMC9025385
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11081275
Stem-Cell Therapy for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) in Newborns
Abstract
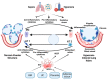
Premature newborns are at a higher risk for the development of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), acute lung injury (ALI) associated with lung inflammation, disruption of alveolar structure, impaired alveolar growth, lung fibrosis, impaired lung angiogenesis, and development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) with severe long-term developmental adverse effects. The current therapy for BPD is limited to supportive care including high-oxygen therapy and pharmacotherapy. Recognizing more feasible treatment options to improve lung health and reduce complications associated with BPD is essential for improving the overall quality of life of premature infants. There is a reduction in the resident stem cells in lungs of premature infants with BPD, which strongly suggests a critical role of stem cells in BPD pathogenesis; this warrants the exploration of the potential therapeutic use of stem-cell therapy. Stem-cell-based therapies have shown promise for the treatment of many pathological conditions including acute lung injury and BPD. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and MSC-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) including exosomes are promising and effective therapeutic modalities for the treatment of BPD. Treatment with MSCs and EVs may help to reduce lung inflammation, improve pulmonary architecture, attenuate pulmonary fibrosis, and increase the survival rate.
Keywords: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; extracellular vesicles; hyperoxia; lung injury; premature infants; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Balasubramaniam V., Mervis C.F., Maxey A.M., Markham N.E., Abman S.H. Hyperoxia Reduces Bone Marrow, Circulating, and Lung Endothelial Progenitor Cells in the Developing Lung: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007;292:L1073–L1084. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00347.2006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bancalari E., infancy A.G.-C. Chronic Lung Disease in Early Infancy. 1st ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 1999. Clinical Course and Lung Function Abnormalities during Development of Neonatal Chronic Lung Disease; pp. 41–64.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

