Which Actigraphy Dimensions Predict Longitudinal Outcomes in Bipolar Disorders?
- PMID: 35456294
- PMCID: PMC9027161
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11082204
Which Actigraphy Dimensions Predict Longitudinal Outcomes in Bipolar Disorders?
Abstract
Bipolar disorder (BD) is characterized by recurrent mood episodes. It is increasingly suggested that disturbances in sleep-wake cycles and/or circadian rhythms could represent valuable predictors of recurrence, but few studies have addressed this question. Euthymic individuals with BD (n = 69) undertook 3 weeks of actigraphy recording and were then followed up for a median duration of 3.5 years. Principal component analyses were used to identify core dimensions of sleep quantity/variability and circadian rhythmicity. Associations between clinical variables and actigraphy dimensions and time to first recurrence were explored using survival analyses, and then using area under the curve (AUC) analyses (early vs. late recurrence). Most participants (64%) experienced a recurrence during follow-up (median survival time: 18 months). After adjusting for potential confounding factors, an actigraphy dimension comprising amplitude and variability/stability of circadian rhythms was a significant predictor of time to recurrence (p = 0.009). The AUC for correct classification of early vs. late recurrence subgroups was only 0.64 for clinical predictors, but combining these variables with objectively measured intra-day variability improved the AUC to 0.82 (p = 0.04). Actigraphy estimates of circadian rhythms, particularly variability/stability and amplitude, may represent valid predictive markers of future BD recurrences and could be putative targets for future psychosocial interventions.
Keywords: actigraphy; bipolar disorder; circadian rhythms; longitudinal; predictors; recurrence; sleep; survival analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
B.E. has received honoraria for consulting from Sanofi. F.B. is an advisor on mental health to the French government. All other authors have no conflict of interest regarding this work.
Figures
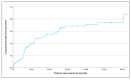
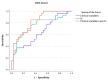
References
-
- Vazquez G.H., Holtzman J.N., Lolich M., Ketter T.A., Baldessarini R.J. Recurrence rates in bipolar disorder: Systematic comparison of long-term prospective, naturalistic studies versus randomized controlled trials. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;25:1501–1512. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.07.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Etain B., Bellivier F., Olie E., Aouizerate B., Aubin V., Belzeaux R., Courtet P., Dubertret C., Schwan R., Roux P., et al. Clinical predictors of recurrences in bipolar disorders type 1 and 2: A FACE-BD longitudinal study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021;134:129–137. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.12.041. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

