Exercise Training in Post-COVID-19 Patients: The Need for a Multifactorial Protocol for a Multifactorial Pathophysiology
- PMID: 35456321
- PMCID: PMC9028177
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11082228
Exercise Training in Post-COVID-19 Patients: The Need for a Multifactorial Protocol for a Multifactorial Pathophysiology
Abstract
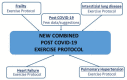
The battle against COVID-19 has entered a new phase with Rehabilitation Centres being among the major players, because the medical outcome of COVID-19 patients does not end with the control of pulmonary inflammation marked by a negative virology test, as many patients continue to suffer from long-COVID-19 syndrome. Exercise training is known to be highly valuable in patients with cardiac or lung disease, and it exerts beneficial effects on the immune system and inflammation. We therefore reviewed past and recent papers about exercise training, considering the multifactorial features characterizing post-COVID-19 patients' clinical conditions. Consequently, we conceived a proposal for a post-COVID-19 patient exercise protocol as a combination of multiple recommended exercise training regimens. Specifically, we built pre-evaluation and exercise training for post-COVID-19 patients taking advantage of the various programs of exercise already validated for diseases that may share pathophysiological and clinical characteristics with long-COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; exercise; training.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Achilleos S., Quattrocchi A., Gabel J., Heraclides A., Kolokotroni O., Constantinou C., Ugarte M.P., Nicolaou N., Rodriguez-Llanes J.M., Bennett C.M., et al. Excess all-cause mortality and COVID-19-related mortality: A temporal analysis in 22 countries, from January until August 2020. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022;51:35–53. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyab123. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jimeno-Almazán A., Pallarés J.G., Buendía-Romero Á., Martínez-Cava A., Franco-López F., Sanchez-Alcaraz Martínez B.J., Bernal-Morel E., Courel-Ibáñez J. Post-COVID-19 Syndrome and the Potential Benefits of Exercise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021;18:5329. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18105329. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barker-Davies R.M., O’Sullivan O., Senaratne K.P.P., Baker P., Cranley M., Dharm-Datta S., Ellis H., Goodall D., Gough M., Lewis S., et al. The Stanford Hall consensus statement for post-COVID-19 rehabilitation. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020;54:949–959. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2020-102596. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y., Coats A.J.S., Zheng Z., Adamo M., Ambrosio G., Anker S.D., Butler J., Xu D., Mao J., Khan M.S., et al. Management of heart failure patients with COVID-19: A joint position paper of the Chinese Heart Failure Association & National Heart Failure Committee and the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020;22:941–956. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1915. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous