SNPs in Genes Related to DNA Damage Repair in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Their Association with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Drug Resistance
- PMID: 35456415
- PMCID: PMC9029044
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13040609
SNPs in Genes Related to DNA Damage Repair in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Their Association with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Drug Resistance
Abstract
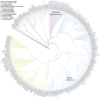
Genes related to DNA damage repair in Mycobacterium tuberculosis are critical for survival and genomic diversification. The aim of this study is to compare the presence of SNPs in genes related to DNA damage repair in sensitive and drug-resistant M. tuberculosis genomes isolated from patients with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We collected 399 M. tuberculosis L4 genomes from several public repositories; 224 genomes belonging to hosts without T2DM, of which 123 (54.9%) had drug sensitive tuberculosis (TB) and 101 (45.1%) had drug resistance (DR)-TB; and 175 genomes from individuals with T2DM, of which 100 (57.1%) had drug sensitive TB and 75 (42.9%) had DR-TB. The presence of SNPs in the coding regions of 65 genes related to DNA damage repair was analyzed and compared with the resistance profile and the presence/absence of T2DM in the host. The results show the phylogenetic relationships of some SNPS and L4 sub-lineages, as well as differences in the distribution of SNPs present in DNA damage repair-related genes related to the resistance profile of the infecting strain and the presence of T2DM in the host. Given these differences, it was possible to generate two discriminant functions to distinguish between drug sensitive and drug resistant genomes, as well as patients with or without T2DM.
Keywords: DNA repair; diabetes mellitus; resistance; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SNPs in genes related to the repair of damage to DNA in clinical isolates of M. tuberculosis: A transversal and longitudinal approach.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 25;19(6):e0295464. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295464. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38917091 Free PMC article.
-
Whole genome sequencing analysis to evaluate the influence of T2DM on polymorphisms associated with drug resistance in M. tuberculosis.BMC Genomics. 2022 Jun 24;23(1):465. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08709-z. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35751020 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective genomic analysis of drug-resistant strains of M. tuberculosis in a high-burden setting, with an emphasis on comparative diagnostics and reactivation and reinfection status.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Jan 7;20(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4739-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31910804 Free PMC article.
-
Focusing on DNA Repair and Damage Tolerance Mechanisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: An Emerging Therapeutic Theme.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(5):390-408. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200110114322. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31924156 Review.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the need for a curated database.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2013 Jan;93(1):30-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2012.11.002. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2013. PMID: 23266261 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sarcopenia and Tuberculosis: Is There Any Connection?J Pers Med. 2023 Jul 6;13(7):1102. doi: 10.3390/jpm13071102. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37511715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis to Assess Mutations in Efflux Pumps in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: The Influence in Drug Resistance.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 4;13(6):1306. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061306. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572193 Free PMC article.
-
SNPs in genes related to the repair of damage to DNA in clinical isolates of M. tuberculosis: A transversal and longitudinal approach.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 25;19(6):e0295464. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295464. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38917091 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Diabetes Mellitus-Tuberculosis and the Generation of Drug Resistance.Microorganisms. 2024 Dec 20;12(12):2649. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122649. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutational Dynamics Related to Antibiotic Resistance in M. tuberculosis Isolates from Serial Samples of Patients with Tuberculosis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Microorganisms. 2024 Feb 3;12(2):324. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020324. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global Tuberculosis Report 2020. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020.
-
- Ponce-De-Leon A., Garcia-Garcia M.D.L., Garcia-Sancho M.C., Gomez-Perez F.J., Valdespino-Gomez J.L., Olaiz-Fernandez G., Rojas R., Ferreyra-Reyes L., Cano-Arellano B., Bobadilla M., et al. Tuberculosis and Diabetes in Southern Mexico. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1584–1590. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.7.1584. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xu Y., Cancino-Muñoz I., Torres-Puente M., Villamayor L.M., Borrás R., Borrás-Máñez M., Bosque M., Camarena J.J., Colomer-Roig E., Colomina J., et al. High-resolution mapping of tuberculosis transmission: Whole genome sequencing and phylogenetic modelling of a cohort from Valencia Region, Spain. PLoS Med. 2019;16:e1002961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002961. - DOI - PMC - PubMed