InsuLock: A Weakly Supervised Learning Approach for Accurate Insulator Prediction, and Variant Impact Quantification
- PMID: 35456427
- PMCID: PMC9026820
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13040621
InsuLock: A Weakly Supervised Learning Approach for Accurate Insulator Prediction, and Variant Impact Quantification
Abstract
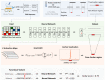
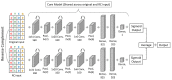
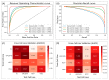
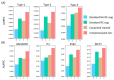
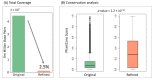
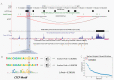
Mapping chromatin insulator loops is crucial to investigating genome evolution, elucidating critical biological functions, and ultimately quantifying variant impact in diseases. However, chromatin conformation profiling assays are usually expensive, time-consuming, and may report fuzzy insulator annotations with low resolution. Therefore, we propose a weakly supervised deep learning method, InsuLock, to address these challenges. Specifically, InsuLock first utilizes a Siamese neural network to predict the existence of insulators within a given region (up to 2000 bp). Then, it uses an object detection module for precise insulator boundary localization via gradient-weighted class activation mapping (~40 bp resolution). Finally, it quantifies variant impacts by comparing the insulator score differences between the wild-type and mutant alleles. We applied InsuLock on various bulk and single-cell datasets for performance testing and benchmarking. We showed that it outperformed existing methods with an AUROC of ~0.96 and condensed insulator annotations to ~2.5% of their original size while still demonstrating higher conservation scores and better motif enrichments. Finally, we utilized InsuLock to make cell-type-specific variant impacts from brain scATAC-seq data and identified a schizophrenia GWAS variant disrupting an insulator loop proximal to a known risk gene, indicating a possible new mechanism of action for the disease.
Keywords: 3D chromatin structure; CTCF mediated insulator loops; brain disorders; deep learning; gene regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lieberman-Aiden E., van Berkum N.L., Williams L., Imakaev M., Ragoczy T., Telling A., Amit I., Lajoie B.R., Sabo P.J., Dorschner M.O., et al. Comprehensive mapping of long-range interactions reveals folding principles of the human genome. Science. 2009;326:289–293. doi: 10.1126/science.1181369. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

