Chromatin Structure and Dynamics: Focus on Neuronal Differentiation and Pathological Implication
- PMID: 35456445
- PMCID: PMC9029427
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13040639
Chromatin Structure and Dynamics: Focus on Neuronal Differentiation and Pathological Implication
Abstract
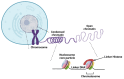
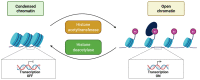
Chromatin structure is an essential regulator of gene expression. Its state of compaction contributes to the regulation of genetic programs, in particular during differentiation. Epigenetic processes, which include post-translational modifications of histones, DNA methylation and implication of non-coding RNA, are powerful regulators of gene expression. Neurogenesis and neuronal differentiation are spatio-temporally regulated events that allow the formation of the central nervous system components. Here, we review the chromatin structure and post-translational histone modifications associated with neuronal differentiation. Studying the impact of histone modifications on neuronal differentiation improves our understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms of chromatinopathies and opens up new therapeutic avenues. In addition, we will discuss techniques for the analysis of histone modifications on a genome-wide scale and the pathologies associated with the dysregulation of the epigenetic machinery.
Keywords: acetylation; chromatin; chromatinopathies; epigenetics; histone modification; methylation; neuronal differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Chromatin in Prostate Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1210:379-407. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-32656-2_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31900918 Review.
-
The Expanding Constellation of Histone Post-Translational Modifications in the Epigenetic Landscape.Genes (Basel). 2021 Oct 10;12(10):1596. doi: 10.3390/genes12101596. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking epigenetics to lipid metabolism: focus on histone deacetylases.Mol Membr Biol. 2012 Nov;29(7):257-66. doi: 10.3109/09687688.2012.729094. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Mol Membr Biol. 2012. PMID: 23095054 Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of epidermal differentiation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014 Feb 1;4(2):a015263. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a015263. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014. PMID: 24492849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between different epigenetic modifications and mechanisms.Adv Genet. 2010;70:101-41. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-380866-0.60005-8. Adv Genet. 2010. PMID: 20920747 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatinopathies: insight in clinical aspects and underlying epigenetic changes.J Appl Genet. 2024 May;65(2):287-301. doi: 10.1007/s13353-023-00824-1. Epub 2024 Jan 5. J Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 38180712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The omics era: a nexus of untapped potential for Mendelian chromatinopathies.Hum Genet. 2024 Apr;143(4):475-495. doi: 10.1007/s00439-023-02560-2. Epub 2023 Apr 28. Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 37115317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Modifications in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium of the Eye During RPE-Related Regeneration or Retinal Diseases in Vertebrates.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 25;13(7):1552. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071552. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Damage and Chromatin Rearrangement Work Together to Promote Neurodegeneration.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan;62(1):1282-1290. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04331-0. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38977621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Chronic Pain.Cells. 2022 Aug 22;11(16):2613. doi: 10.3390/cells11162613. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36010687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

