Phenotype Expansion for Atypical Gaucher Disease Due to Homozygous Missense PSAP Variant in a Large Consanguineous Pakistani Family
- PMID: 35456468
- PMCID: PMC9028228
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13040662
Phenotype Expansion for Atypical Gaucher Disease Due to Homozygous Missense PSAP Variant in a Large Consanguineous Pakistani Family
Abstract
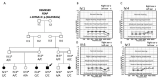
Atypical Gaucher disease is caused by variants in the PSAP gene. Saposin C is one of four homologous proteins derived from sequential cleavage of the saposin precursor protein, prosaposin. It is an essential activator for glucocerebrosidase, which is deficient in Gaucher disease. Although atypical Gaucher disease due to deficiency of saposin C is rare, it exhibits vast phenotypic heterogeneity. Here, we report on a Pakistani family that exhibits features of Gaucher disease, i.e., prelingual profound sensorineural hearing impairment, vestibular dysfunction, hepatosplenomegaly, kyphosis, and thrombocytopenia. The family was investigated using exome and Sanger sequencing. A homozygous missense variant c.1076A>C: p.(Glu359Ala) in exon 10 of the PSAP gene was observed in all affected family members. In conclusion, we identified a new likely pathogenic missense variant in PSAP in a large consanguineous Pakistani family with atypical Gaucher disease. Gaucher disease due to a deficiency of saposin C has not been previously reported within the Pakistani population. Genetic screening of patients with the aforementioned phenotypes could ensure adequate follow-up and the prevention of further complications. Our finding expands the genetic and phenotypic spectrum of atypical Gaucher disease due to a saposin C deficiency.
Keywords: atypical Gaucher disease; exome sequencing; hearing impairment; saposin C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chérin P., Rose C., De Roux-Serratrice C., Tardy D., Dobbelaere D., Grosbois B., Hachulla E., Jaussaud R., Javier R.-M., Noël E., et al. The neurological manifestations of Gaucher disease type 1: The French Observatoire on Gaucher disease (FROG) J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010;33:331–338. doi: 10.1007/s10545-010-9095-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

