Genetic Polymorphisms of IGF1 and IGF1R Genes and Their Effects on Growth Traits in Hulun Buir Sheep
- PMID: 35456472
- PMCID: PMC9031115
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13040666
Genetic Polymorphisms of IGF1 and IGF1R Genes and Their Effects on Growth Traits in Hulun Buir Sheep
Abstract
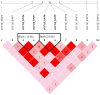
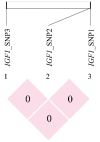
The identification of candidate genes and genetic variations associated with growth traits is important for sheep breeding. Insulin like growth factor 1 (IGF1) and insulin like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) are well-accepted candidate genes that affect animal growth and development. The current study attempted to assess the association between IGF1 and IGF1R genetic polymorphisms and growth traits in Hulun Buir sheep. To achieve this goal, we first identified three and ten single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in exons of IGF1 and IGF1R in Hulun Buir sheep and then constructed six haplotypes of IGF1R based on linkage disequilibrium, respectively. Association studies were performed between SNPs and haplotypes of IGF1 and IGF1R with twelve growth traits in a population encompassing 229 Hulun Buir sheep using a general linear model. Our result indicated three SNPs in IGF1 were significantly associated with four growth traits (p < 0.05). In IGF1R, three SNPs and two haplotype blocks were significantly associated with twelve growth traits (p < 0.05). The combined haplotype H5H5 and H5H6 in IGF1R showed the strong association with 12 superior growth traits in Hulun Buir sheep (p < 0.05). In conclusion, we identified SNPs and haplotype combinations associated with the growth traits, which provided genetic resources for marker-assisted selection (MAS) in Hulun Buir sheep breeding.
Keywords: Chinese indigenous sheep; IGF1; IGF1R; association analysis; growth traits; haplotype.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
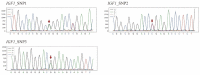
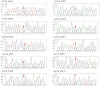
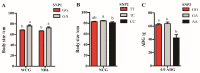
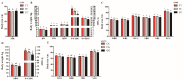
References
-
- Luo W.W., Zhou Y., Wang J.R., Yu X.M., Tong J.G. Identifying Candidate Genes Involved in the Regulation of Early Growth Using Full-Length Transcriptome and RNA-Seq Analyses of Frontal and Parietal Bones and Vertebral Bones in Bighead Carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) Front. Genet. 2021;11:603454. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.603454. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- XU S.S., Li M.H. Recent advances in understanding genetic variants associated with economically important traits in sheep (Ovis aries) revealed by high-throughput screening technologies. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2017;4:25–34. doi: 10.15302/J-FASE-2017151. - DOI
-
- Valencia C.P.L., Franco L., Herrera D.H. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the CAPN, CAST, LEP, GH, and IGF-1 genes with growth parameters and ultrasound characteristics of the Longissimus dorsi muscle in Colombian hair sheep. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022;54:82. doi: 10.1007/s11250-022-03086-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kindler J.M., Pollock N.K., Laing E.M., Jenkins N.T., Oshri A., Isales C., Hamrick M., Lewis R.D. Insulin Resistance Negatively Influences the Muscle-Dependent IGF-1-Bone Mass Relationship in Premenarcheal Girls. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016;101:199–205. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3451. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

