Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Sulfadiazine and Its Metabolite N4-Acetyl Sulfadiazine in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) at Different Temperatures after Oral Administration
- PMID: 35456543
- PMCID: PMC9025148
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040712
Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Sulfadiazine and Its Metabolite N4-Acetyl Sulfadiazine in Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) at Different Temperatures after Oral Administration
Abstract
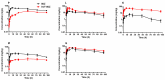
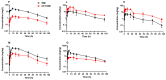
In this study, the plasma pharmacokinetics and tissue disposition of sulfadiazine (SDZ) and its main metabolite, N4-acetyl sulfadiazine (ACT-SDZ), were compared between 18 and 24 °C following a single oral administration of SDZ at 50 mg/kg in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). The plasma and tissues were sampled from 0.167 h up to 96 h and analyzed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography with an ultraviolet detector. The pharmacokinetic parameters were estimated using a one-compartmental approach. Results showed that pharmacokinetics of SDZ and ACT-SDZ in plasma and tissues were notably influenced by the increase of temperature. The increased temperature shortened the absorption half-life (K01_HL) of SDZ and ACT-SDZ in gill, kidney, and plasma, but increased in liver and muscle + skin. The elimination half-life (K10_HF) and the area under concentration-time curve (AUC0-∞) of SDZ and ACT-SDZ all presented a declined trend. The apparent volume of distribution (V_F) of SDZ in plasma was increased from 0.93 to 1.64 L/kg, and the apparent systemic total body clearance (Cl_F) was also increased from 0.01 to 0.05 L/h/kg. Overall, the rise of temperature decreased K10_HF, AUC0-∞ of SDZ, and ACT-SDZ in plasma and tissues, but increased V_F and Cl_F in the plasma for SDZ.
Keywords: N4-acetyl sulfadiazine; grass carp; pharmacokinetics; sulfadiazine; temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gustafsson A., Båverud V., Franklin A., Gunnarsson A., Ogren G., Ingvast-Larsson C. Repeated administration of trimethoprim/sulfadiazine in the horse—pharmacokinetics, plasma protein binding and influence on the intestinal microflora. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999;22:20–26. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2885.1999.00183.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zorrilla I., Chabrillon M., Arijo S., Diaz-Rosales P., Martinez-Manzanares E., Balebona M.C., Morinigo M.A. Bacteria recovered from diseased cultured gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) in southwestern Spain. Aquaculture. 2003;218:11–20. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00309-5. - DOI
-
- Plumb J.A., Maestrone G., Quinlan E. Use of a potentiated sulfonamide to control Edwardsiella ictaluri infection in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Aquaculture. 1987;62:187–194. doi: 10.1016/0044-8486(87)90165-7. - DOI
-
- Samuelsen O.B., Pursell L., Smith P., Ervik A. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetic study of Romet30 in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and in vitro antibacterial activity against Aeromonas salmonicida. Aquaculture. 1997;152:13–24. doi: 10.1016/S0044-8486(96)01508-6. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

