Neuroprotective Effect of Ramipril Is Mediated by AT2 in a Mouse MODEL of Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
- PMID: 35456682
- PMCID: PMC9030366
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040848
Neuroprotective Effect of Ramipril Is Mediated by AT2 in a Mouse MODEL of Paclitaxel-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
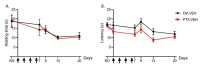
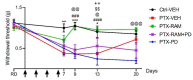
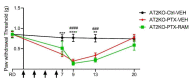
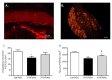
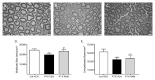
Paclitaxel (PTX)-induced peripheral neuropathy (PIPN) induces numerous symptoms affecting patient quality of life, leading to decreased doses or even to cessation of anticancer therapy. Previous studies have reported that a widely used drug, ramipril, improves neuroprotection in several rodent models of peripheral neuropathy. The protective role of the angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2) in the central and peripheral nervous systems is well-established. Here, we evaluate the effects of ramipril in the prevention of PIPN and the involvement of AT2 in this effect. Paclitaxel was administered in wild type or AT2-deficient mice on alternate days for 8 days, at a cumulative dose of 8 mg/kg (2 mg/kg per injection). Ramipril, PD123319 (an AT2 antagonist), or a combination of both were administered one day before PTX administration, and daily for the next twenty days. PTX-administered mice developed mechanical allodynia and showed a loss of sensory nerve fibers. Ramipril prevented the functional and morphological alterations in PTX mice. The preventive effect of ramipril against tactile allodynia was completely absent in AT2-deficient mice and was counteracted by PD123319 administration in wild type mice. Our work highlights the potential of ramipril as a novel preventive treatment for PIPN, and points to the involvement of AT2 in the neuroprotective role of ramipril in PIPN.
Keywords: Ramipril; angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; mouse model; neuropathic pain; paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kerckhove N., Collin A., Condé S., Chaleteix C., Pezet D., Balayssac D. Long-term effects, pathophysiological mechanisms, and risk factors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathies: A comprehensive literature review. Front. Pharmacol. 2017;8:1–17. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00086. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Danigo A., Rovini A., Bessaguet F., Bouchenaki H., Bernard A., Sturtz F., Bourthoumieu S., Desmoulière A., Magy L., Demiot C. The Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor, a Target for Protection and Regeneration of the Peripheral Nervous System? Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14:175. doi: 10.3390/ph14030175. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

