Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase: A Review of This Enzyme Role in the Intestinal Barrier Function
- PMID: 35456797
- PMCID: PMC9026380
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10040746
Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase: A Review of This Enzyme Role in the Intestinal Barrier Function
Abstract
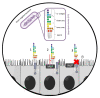
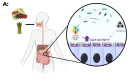
Intestinal alkaline phosphatase (IALP) has recently assumed a special relevance, being the subject of study in the prevention and treatment of certain diseases related to leaky gut. This brush border enzyme (ecto-enzyme) plays an important role in the maintenance of intestinal microbial homeostasis and intestinal barrier function through its ability to dephosphorylate lipopolysaccharide (LPS). This review addresses how IALP and intestinal barrier dysfunction may be implicated in the pathophysiology of specific diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease, necrotizing enterocolitis, and metabolic syndrome. The use of IALP as a possible biomarker to assess intestinal barrier function and strategies to modulate IALP activity are also discussed.
Keywords: inflammatory bowel disease; intestinal alkaline phosphatase; intestinal barrier function; low-grade chronic inflammation; metabolic dysfunction; necrotizing enterocolitis; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Suzuki U.Y.K., Takashi M. Uber ein enzyme–phytase‖ das anhydro-oxy-methylen-diphosphorsaure spaltet. Bull. Coll. Agric. Tokyo Imp. Univ. 1907;7:503–512.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

