Mechano Growth Factor Accelerates ACL Repair and Improves Cell Mobility of Mechanically Injured Human ACL Fibroblasts by Targeting Rac1-PAK1/2 and RhoA-ROCK1 Pathways
- PMID: 35457148
- PMCID: PMC9026312
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23084331
Mechano Growth Factor Accelerates ACL Repair and Improves Cell Mobility of Mechanically Injured Human ACL Fibroblasts by Targeting Rac1-PAK1/2 and RhoA-ROCK1 Pathways
Abstract
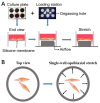
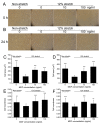
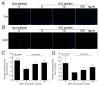
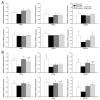
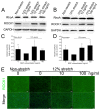
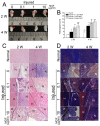
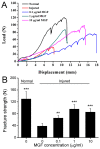
Exceeded mechanical stress leads to a sublethal injury to anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) fibroblasts, and it will hinder cell mobility and ACL regeneration, and even induce osteoarthritis. The mechano growth factor (MGF) could be responsible for mechanical stress and weakening its negative effects on cell physiological behaviors. In this study, effects of MGF on cell mobility and relevant molecules expression in injured ACL fibroblasts were detected. After an injurious mechanical stretch, the analysis carried out, at 0 and 24 h, respectively, showed that the cell area, roundness, migration, and adhesion of ACL fibroblasts were reduced. MGF (10, 100 ng/mL) treatment could improve cell area, roundness and promote cell migration and adhesion capacity compared with the injured group without MGF. Further study indicated that cell mobility-relevant molecules (PAK1/2, Cdc42, Rac1, RhoA, and ROCK1) expression in ACL fibroblasts was down-regulated at 0 or 24 h after injurious stretch (except Rac1 and RhoA at 0 h). Similarly, MGF improved cell mobility-relevant molecule expression, especially the ROCK1 expression level in ACL fibroblasts at 0 or 24 h after injurious stretch. Protein expression of ROCK1 in injured ACL fibroblasts was also reduced and could be recovered by MGF treatment. In a rabbit partial ACL transection (ACLT) model, ACL exhibited poor regenerative capacity in collagen and extracellular matrix (ECM) synthesis after partial ACLT for 2 or 4 weeks, and MGF remarkably accelerated ACL regeneration and restored its mechanical loading capacity after partial ACLT for four weeks. Our findings suggest that MGF weakens the effects of pathological stress on cell mobility of ACL fibroblasts and accelerates ACL repair, and might be applied as a future treatment approach to ACL rupture in the clinic.
Keywords: anterior cruciate ligament; cell adhesion; cell migration; fracture strength; mechano growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MGF E peptide pretreatment improves collagen synthesis and cell proliferation of injured human ACL fibroblasts via MEK-ERK1/2 signaling pathway.Growth Factors. 2017 Feb;35(1):29-38. doi: 10.1080/08977194.2017.1327856. Epub 2017 May 29. Growth Factors. 2017. PMID: 28553731
-
MGF E peptide improves anterior cruciate ligament repair by inhibiting hypoxia-induced cell apoptosis and accelerating angiogenesis.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):8846-8861. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27546. Epub 2018 Oct 14. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30317597
-
Mechano growth factor pretreatment yield mechanical stimuli induced cell stress responses in ligament fibroblasts of osteoarthritis via activating ATF-2.Biotechnol Lett. 2020 Aug;42(8):1337-1349. doi: 10.1007/s10529-020-02866-5. Epub 2020 Mar 28. Biotechnol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32222864
-
A Systematic Review of Basic Science and Animal Studies on the Use of Doxycycline to Reduce the Risk of Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture/Transection.Am J Sports Med. 2021 Jul;49(8):2255-2261. doi: 10.1177/0363546520965971. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Am J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 33216621
-
FilGAP and its close relatives: a mediator of Rho-Rac antagonism that regulates cell morphology and migration.Biochem J. 2013 Jul 1;453(1):17-25. doi: 10.1042/BJ20130290. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23763313 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanome-Guided Strategies in Regenerative Rehabilitation.Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2024 Mar;29:100516. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2023.100516. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 38586151 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydrocorydaline Accelerates Cell Proliferation and Extracellular Matrix Synthesis of TNFα-Treated Human Chondrocytes by Targeting Cox2 through JAK1-STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 30;23(13):7268. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137268. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806272 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical force regulates the paracrine functions of ADSCs to assist skin expansion in rats.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Aug 13;15(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03822-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39135129 Free PMC article.
-
Subchondral injection of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates knee osteoarthritis by inhibiting osteoblast apoptosis and TGF-beta activity.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 May 9;16(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04366-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40346614 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Death in Acute Organ Injury and Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 1;25(7):3930. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073930. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612740 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

