Psoriasis and Systemic Inflammatory Disorders
- PMID: 35457278
- PMCID: PMC9028262
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23084457
Psoriasis and Systemic Inflammatory Disorders
Abstract
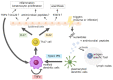
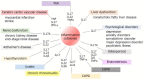
Psoriasis is a representative inflammatory skin disease occupied by large surface involvement. As inflammatory cells and cytokines can systemically circulate in various organs, it has been speculated that psoriatic skin inflammation influences the systemic dysfunction of various organs. Recent updates of clinical studies and experimental studies showed the important interaction of psoriasis to systemic inflammatory diseases. Furthermore, the importance of systemic therapy in severe psoriasis is also highlighted to prevent the development of systemic inflammatory diseases. In this review, we introduced representative systemic inflammatory diseases associated with psoriasis and the detailed molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: IL-17; TNF-α; inflammation; organs; psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tomura M., Honda T., Tanizaki H., Otsuka A., Egawa G., Tokura Y., Waldmann H., Hori S., Cyster J.G., Watanabe T., et al. Activated regulatory T cells are the major T cell type emigrating from the skin during a cutaneous immune response in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010;120:883–893. doi: 10.1172/JCI40926. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gray E.E., Ramírez-Valle F., Xu Y., Wu S., Wu Z., Karjalainen K.E., Cyster J.G. Deficiency in IL-17-committed Vγ4(+) γδ T cells in a spontaneous Sox13-mutant CD45.1(+) congenic mouse substrain provides protection from dermatitis. Nat. Immunol. 2013;14:584–592. doi: 10.1038/ni.2585. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

