Implementation of a Psychiatric Consultation for Healthcare Workers during First Wave of COVID-19 Outbreak
- PMID: 35457653
- PMCID: PMC9025663
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19084780
Implementation of a Psychiatric Consultation for Healthcare Workers during First Wave of COVID-19 Outbreak
Abstract
Background: Prevention and management strategies of mental suffering in healthcare workers appeared as important challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic. This article aims to: (1) show how potential psychiatric disorders for healthcare workers (HCW) during the first wave of the COVID-19 outbreak were identified; (2) present an activity report of this consultation; and (3) analyze and learn from this experience for the future.
Methods: We performed a retrospective quantitative analysis of socio-demographic and clinical data, in addition to psychiatric scales scores for the main potential psychiatric risks (PDI, PDEQ, PCL-5, HADS, MBI-HSS) and post-hoc qualitative analysis of written interviews.
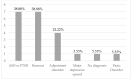
Results: Twenty-five healthcare workers consulted between 19 March 2020 and 12 June 2020. We found 78.57% presented high peritraumatic dissociation and peritraumatic distress, 68.75% had severe anxiety symptoms, and 31.25% had severe depression symptoms. Concerning burnout, we found that 23.53% had a high level of emotional exhaustion. In the qualitative analysis of the written interview, we found a direct link between stress and the COVID-19 pandemic, primarily concerning traumatic stressors, and secondarily with work-related stress.
Conclusions: Early detection of traumatic reactions, valorization of individual effort, and limitations on work overload appear like potential key preventive measures to prevent psychiatric complications for healthcare workers in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD); burnout; healthcare workers; psychiatric consultation; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- John Hopkins University of Medicine Coronavirus Ressource Center. [(accessed on 17 May 2021)]. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- Office Fédéral de la Santé Publique Cas Confirmés en Laboratoire. [(accessed on 17 May 2021)]. Available online: https://www.covid19.admin.ch/fr/epidemiologic/case.
-
- World Health Organization Interim Briefing Note—Taking into Account the Psychosocial and Mental Health Aspects of the COVID-19 Epidemic. 2020. [(accessed on 17 March 2020)]. Available online: https://interagencystandingcommittee.org/iasc-referencegroup-mental-heal....
-
- Pappa S., Ntella V., Giannakas T., Giannakoulis V.G., Papoutsi E., Katsaounou P. Prevalence of depression, anxiety, and insomnia among healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020;88:901–907. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical