Stroke Risk Factors of Stroke Patients in China: A Nationwide Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 35457673
- PMCID: PMC9030671
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19084807
Stroke Risk Factors of Stroke Patients in China: A Nationwide Community-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Stroke is the leading cause of death in China, and its burdens are rapidly increasing. The prevalence and control of stroke risk factors among stroke patients in China are unknown.
Objective: We investigated the stroke risk factors of stroke patients in China.
Design: We examined stroke risk factors in 6580 stroke patients aged 18 years or older in the China National Chronic Diseases and Nutrition Surveillance of Adults (2015-2017). With regard to the basic characteristics of the study participants, categorical variables were described as frequency (percent). The chi-square test was used to analyze the difference between men and women. The multivariate logistic regression model was used in the multivariate analysis.
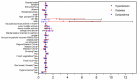
Results: Among the 6580 stroke patients, hypertension was the most common stroke risk factor identified in most cases (78.51%), followed by overweight or obesity (61.58%), dyslipidemia (54.38%), smoking (24.04%), diabetes (21.75%), family history of stroke (17.43%), lack of exercise (16.35%), and atrial fibrillation (4.47%). Drinking stroke patients had a lower rate of hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Patients with hyperuricemia had a higher rate of hypertension and dyslipidemia than no-hyperuricemia patients. The hypertension awareness, treatment, and control rates among hypertension stroke patients were 73.62%, 70.19%, and 17.79%, respectively. The diabetes awareness, treatment, and control rates among diabetes patients were 69.74%, 65.83%, and 34.59%, respectively. The dyslipidemia awareness, treatment, and control rates among dyslipidemia patients were 42.37%, 29.4%, and 20.07%, respectively. Among treated hypertension patients, the rates of taking medicine as medically advised, controlled diet, increased exercise, and blood pressure monitoring were 91.31%, 58.88%, 45.78%, and 73.99%, respectively. Among treated diabetes patients, the rates of oral antidiabetic medications, insulin injection, diet control, and blood glucose monitoring were 78.24%, 34.71%, 85.77%, and 78.24%, respectively. Among treated dyslipidemic patients, the rate of taking medicine as medical advice, controlled diet, increased exercise, and regular blood lipid monitoring was 80.61%, 77.57%, 56.46%, and 40.3%, respectively.
Conclusions: The most common risk factors for community stroke patients in China are hypertension, dyslipidemia, and overweight or obesity. The stroke community patients' suboptimal awareness and treatment of hypertension, and suboptimal awareness, treatment, and control of diabetes, and dyslipidemia are significant problems in China.
Keywords: China; stroke patients; stroke risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Feigin V.L., Forouzanfar M.H., Krishnamurthi R., Mensah G.A., Connor M., Bennett D.A., Moran A.E., Sacco R.L., Anderson L., Truelsen T., et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2014;383:245–254. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61953-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical