Influence of Obesity on Bone Turnover Markers and Fracture Risk in Postmenopausal Women
- PMID: 35458178
- PMCID: PMC9029584
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14081617
Influence of Obesity on Bone Turnover Markers and Fracture Risk in Postmenopausal Women
Abstract
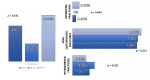
Background and aims: The relationship between obesity and bone metabolism is controversial. In recent decades, the protective role of obesity in the development of osteoporosis is questioned. The aims of this study are the following: to evaluate the differences in bone turnover markers between postmenopausal women with and without obesity and to compare the risk of fracture at five years between these groups. Methods: An observational longitudinal prospective cohort study of postmenopausal women with obesity (O) (body mass index (BMI) > 30 kg/m2) and non-obesity (NoO) (BMI < 30 kg/m2) is designed. 250 postmenopausal women are included in the study (NoO: 124 (49.6%) and O: 126 (50.4%)). It measures epidemiological variables, dietary variables (calcium intake, vitamin D intake, smoking, alcohol consumption, and physical activity), biochemicals (β-crosslap, type I procollagen amino-terminal peptide (P1NP), 25OH-vitamin D, and parathyroid hormone (PTH)), anthropometric variables, and fracture data five years after the start of the study. The mean age is 56.17 (3.91) years. Women with obesity showed lower levels of vitamin D (O: 17.27 (7.85) ng/mL, NoO: 24.51 (9.60) ng/mL; p < 0.01), and higher levels of PTH (O: 53.24 (38.44−65.96) pg/mL, NoO: 35.24 (25.36−42.40) pg/mL; p < 0.01). Regarding the bone formation marker (P1NP), it was found to be high in women without obesity, O: 45.46 (34.39−55.16) ng/mL, NoO: 56.74 (45.34−70.74) ng/mL; p < 0.01; the bone resorption marker (β-crosslap) was found to be high in women with obesity, being significant in those older than 59 years (O: 0.39 (0.14) ng/mL, NoO 0.24 (0.09) ng/mL; p < 0.05). No differences are observed in the risk of fracture at 5 years based on BMI (OR = 0.90 (95%CI 0.30−2.72); p = 0.85). Conclusions: Postmenopausal women with obesity showed lower levels of bone formation markers; older women with obesity showed higher markers of bone resorption.
Keywords: bone metabolism; bone turnover markers; fracture; obesity; osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ström O., Borgström F., Kanis J.A., Compston J., Cooper C., McCloskey E.V., Jönsson B. Osteoporosis: Burden, health care provision and opportunities in the EU: A report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA) Arch. Osteoporos. 2011;6:59–155. doi: 10.1007/s11657-011-0060-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hernlund E., Svedbom A., Ivergård M., Compston J., Cooper C., Stenmark J., McCloskey E.V., Jönsson B., Kanis J.A. Osteoporosis in the European Union: Medical management, epidemiology and economic burden. A report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA) Arch. Osteoporos. 2013;8:136. doi: 10.1007/s11657-013-0136-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical