Acute Effects of Kawakawa (Piper excelsum) Intake on Postprandial Glycemic and Insulinaemic Response in a Healthy Population
- PMID: 35458200
- PMCID: PMC9032225
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14081638
Acute Effects of Kawakawa (Piper excelsum) Intake on Postprandial Glycemic and Insulinaemic Response in a Healthy Population
Abstract
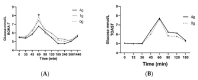
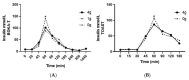
Background: Piper excelsum (kawakawa) is an endemic shrub of Aotearoa, New Zealand, of cultural and medicinal importance to Māori. Its fruits and leaves are often consumed. These tissues contain several compounds that have been shown to be biologically active and which may underpin its putative health-promoting effects. The current study investigates whether kawakawa tea can modulate postprandial glucose metabolism. Methods: We report a pilot three-arm randomized crossover study to assess the bioavailability of kawakawa tea (BOKA-T) in six male participants with each arm having an acute intervention of kawakawa tea (4 g/250 mL water; 1 g/250 mL water; water) and a follow-up two-arm randomized crossover study to assess the impact of acute kawakawa tea ingestion on postprandial glucose metabolism in healthy human volunteers (TOAST) (4 g/250 mL water; and water; n = 30 (15 male and 15 female)). Participants consumed 250 mL of kawakawa tea or water control within each study prior to consuming a high-glycemic breakfast. Pre- and postprandial plasma glucose and insulin concentrations were measured, and the Matsuda index was calculated to measure insulin sensitivity. Results: In the BOKA-T study, lower plasma glucose (p < 0.01) and insulin (p < 0.01) concentrations at 60 min were observed after consumption of a high-dose kawakawa tea in comparison to low-dose or water. In the TOAST study, only plasma insulin (p = 0.01) was lower at 60 min in the high-dose kawakawa group compared to the control group. Both studies showed a trend towards higher insulin sensitivity in the high-dose kawakawa group compared to water only. Conclusions: Consuming kawakawa tea may modulate postprandial glucose metabolism. Further investigations with a longer-term intervention study are warranted.
Keywords: Māori traditional medicine; insulin sensitivity; kawakawa; plasma insulin; postprandial.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hodge S., Keesing V., Wratten S.D., Lövei G.L., Palmer J., Çilgi T. Herbivore Damage and Leaf Loss in the New Zealand Pepper Tree (“kawakawa”; Macropiper excelsum; Piperaceae) N. Z. J. Ecol. 1998;22:173–180.
-
- Briggs L.H. The Essential Oil of Macropiper excelsum (Kawakawa) J. Soc. Chem. Ind. 1941;60:210–212. doi: 10.1002/jctb.5000600709. - DOI
-
- Obst K., Lieder B., Reichelt K.V., Backes M., Paetz S., Geißler K., Krammer G., Somoza V., Ley J.P., Engel K.H. Sensory Active Piperine Analogues from Macropiper excelsum and Their Effects on Intestinal Nutrient Uptake in Caco-2 Cells. Phytochemistry. 2017;135:181–190. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.12.016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

