PAGE-B and REACH-B Predicts the Risk of Developing Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients from Northeast, Brazil
- PMID: 35458462
- PMCID: PMC9033073
- DOI: 10.3390/v14040732
PAGE-B and REACH-B Predicts the Risk of Developing Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients from Northeast, Brazil
Abstract
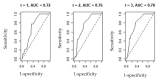
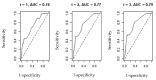
This study aims to evaluate the accuracy of the PAGE-B and REACH-B scores in predicting the risk of developing HCC in patients with chronic hepatitis B regularly followed up at a reference service in the State of Maranhão. A historical, longitudinal, retrospective cohort study, carried out from the review of medical records of patients with chronic Hepatitis B. PAGE-B and REACH-B scores were calculated and the accuracy of the scores in predicting the risk of HCC in the studied population was evaluated. A total of 978 patients were included, with a median age of around 47 years, most of them female and not cirrhotic. HCC was identified in 34 patients. Thrombocytopenia, high viral load, male gender and age were associated with the occurrence of HCC. The ROC curve for the PAGE-B score showed a value of 0.78 and for the REACH-B score of 0.79. The cutoff point for PAGE-B was 11 points for greater sensitivity and for REACH-B 7.5 points considering greater sensitivity and 9.5 points considering greater specificity. PAGE-B and REACH-B scores were able to predict the risk of developing HCC in the studied population. The use of risk stratification scores is useful to reduce costs associated with HCC screening.
Keywords: PAGE-B; REACH-B; chronic hepatitis B; hepatocellular carcinoma; prevalence; surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reassessing the accuracy of PAGE-B-related scores to predict hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis B.J Hepatol. 2020 May;72(5):847-854. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.12.005. Epub 2019 Dec 16. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31857194
-
Validation of the PAGE-B score to predict hepatocellular carcinoma risk in caucasian chronic hepatitis B patients on treatment.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Feb 14;28(6):665-674. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i6.665. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35317422 Free PMC article.
-
External validation of hepatocellular carcinoma risk scores in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection in China.J Viral Hepat. 2021 Oct;28(10):1373-1380. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13569. Epub 2021 Jul 22. J Viral Hepat. 2021. PMID: 34218498
-
Clinical utility of hepatocellular carcinoma risk scores in chronic hepatitis B.Liver Int. 2020 Mar;40(3):484-495. doi: 10.1111/liv.14334. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Liver Int. 2020. PMID: 31884726 Review.
-
Risk prediction of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of antiviral therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Oct 21;19(39):6515-22. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i39.6515. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24151375 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of PAGE-B Score for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients: Reliability, Validity, and Responsiveness.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 5;12(6):1260. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061260. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum protein biomarkers for HCC risk prediction in HIV/HBV co-infected people: a clinical proteomic study using mass spectrometry.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 10;14:1282469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1282469. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022651 Free PMC article.
-
The Cost-Effectiveness of Tenofovir Alafenamide for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus in Taiwan.MDM Policy Pract. 2025 Mar 29;10(1):23814683251328659. doi: 10.1177/23814683251328659. eCollection 2025 Jan-Jun. MDM Policy Pract. 2025. PMID: 40162197 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-HBV Coinfection-Current Challenges for Virologic Monitoring.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 28;11(5):1306. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051306. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37238976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Predictive Scores PAGE-B and mPAGE-B among Brazilian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection.Viruses. 2022 Sep 5;14(9):1968. doi: 10.3390/v14091968. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hosaka T., Suzuki F., Kobayashi M., Seko Y., Kawamura Y., Sezaki H., Akuta N., Suzuki Y., Saitoh S., Arase Y., et al. Long-term entecavir treatment reduces hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2013;58:98–107. doi: 10.1002/hep.26180. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical