Defining the Role of Isoeugenol from Ocimum tenuiflorum against Diabetes Mellitus-Linked Alzheimer's Disease through Network Pharmacology and Computational Methods
- PMID: 35458596
- PMCID: PMC9025232
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27082398
Defining the Role of Isoeugenol from Ocimum tenuiflorum against Diabetes Mellitus-Linked Alzheimer's Disease through Network Pharmacology and Computational Methods
Abstract
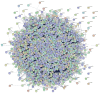
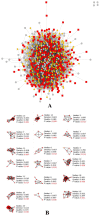
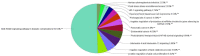
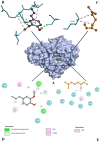
The present study involves the integrated network pharmacology and phytoinformatics-based investigation of phytocompounds from Ocimum tenuiflorum against diabetes mellitus-linked Alzheimer's disease. It aims to investigate the mechanism of the Ocimum tenuiflorum phytocompounds in the amelioration of diabetes mellitus-linked Alzheimer's disease through network pharmacology, druglikeness and pharmacokinetics, molecular docking simulations, GO analysis, molecular dynamics simulations, and binding free energy analyses. A total of 14 predicted genes of the 26 orally bioactive compounds were identified. Among these 14 genes, GAPDH and AKT1 were the most significant. The network analysis revealed the AGE-RAGE signaling pathway to be a prominent pathway linked to GAPDH with 50.53% probability. Upon the molecular docking simulation with GAPDH, isoeugenol was found to possess the most significant binding affinity (-6.0 kcal/mol). The molecular dynamics simulation and binding free energy calculation results also predicted that isoeugenol forms a stable protein-ligand complex with GAPDH, where the phytocompound is predicted to chiefly use van der Waal's binding energy (-159.277 kj/mol). On the basis of these results, it can be concluded that isoeugenol from Ocimum tenuiflorum could be taken for further in vitro and in vivo analysis, targeting GAPDH inhibition for the amelioration of diabetes mellitus-linked Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: AGE-RAGE; Alzheimer’s disease; GAPDH; GO analysis; Ocimum tenuiflorum; binding free energy analysis; diabetes mellitus; druglikeness and pharmacokinetics; isoeugenol; molecular docking simulation; molecular dynamics simulation; network pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Arnold S.E., Arvanitakis Z., Macauley-Rambach S.L., Koenig A.M., Wang H.Y., Ahima R.S., Craft S., Gandy S., Buettner C., Stoeckel L.E., et al. Brain insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer disease: Concepts and conundrums. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018;14:168–181. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2017.185. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

