RETRACTED: An Extensive Pharmacological Evaluation of New Anti-Cancer Triterpenoid (Nummularic Acid) from Ipomoea batatas through In Vitro, In Silico, and In Vivo Studies
- PMID: 35458672
- PMCID: PMC9030838
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27082474
RETRACTED: An Extensive Pharmacological Evaluation of New Anti-Cancer Triterpenoid (Nummularic Acid) from Ipomoea batatas through In Vitro, In Silico, and In Vivo Studies
Retraction in
-
RETRACTED: Majid et al. An Extensive Pharmacological Evaluation of New Anti-Cancer Triterpenoid (Nummularic Acid) from Ipomoea batatas through In Vitro, In Silico, and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2022, 27, 2474.Molecules. 2025 May 27;30(11):2330. doi: 10.3390/molecules30112330. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40434199 Free PMC article.
Abstract
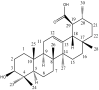
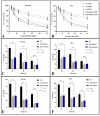
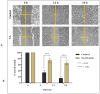
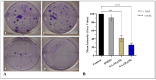
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common cancer in men, accounting for approximately 10% of all new cases in the United States. Plant-derived bioactive compounds, such as pentacyclic triterpenoids (PTs), have the ability to inhibit PCa cell proliferation. We isolated and characterized nummularic acid (NA), a potent PT, as a major chemical constituent of Ipomoea batatas, a medicinal food plant used in ethnomedicine for centuries. In the current study, in vitro antiproliferative potential against PCa cells (DU145 and PC3) via 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay; Western blot protein expression analysis; absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion (ADME); pharmacokinetic prediction studies; and bisphenol A (BPA)-induced prostate inhibition in Sprague Dawley rats were conducted to gauge the anti-cancer ability of NA. Significant (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01) time- and dose-dependent reductions in proliferation of PCa cells, reduced migration, invasion, and increased apoptotic cell population were recorded after NA treatment (3−50 µM). After 72 h of treatment, NA displayed significant IC50 of 21.18 ± 3.43 µM against DU145 and 24.21 ± 3.38 µM against PC3 cells in comparison to the controls cabazitaxel (9.56 ± 1.45 µM and 12.78 ± 2.67 µM) and doxorubicin (10.98 ± 2.71 µM and 15.97 ± 2.77 µM). Further deep mechanistic studies reveal that NA treatment considerably increased the cleavage of caspases and downstream PARP, upregulated BAX and P53, and downregulated BCL-2 and NF-κB, inducing apoptosis in PCa cells. Pharmacokinetic and ADME characterization indicate that NA has a favorable physicochemical nature, with high gastrointestinal absorption, low blood−brain barrier permeability, no hepatotoxicity, and cytochrome inhibition. BPA-induced perturbations of prostate glands in Sprague Dawley rats show a potential increase (0.478 ± 0.28 g) in prostate weight compared to the control (0.385 ± 0.13 g). Multi-dose treatment with NA (10 mg/kg) significantly reduced the prostate size (0.409 ± 0.21 g) in comparison to the control. NA-treated groups exhibited substantial restoration of hematological and histological parameters, reinstatement of serum hormones, and suppression of inflammatory markers. This multifaceted analysis suggests that NA, as a novel small molecule with a strong pharmacokinetic and pharmacological profile, has the potential to induce apoptosis and death in PCa cells.
Keywords: BAX; apoptosis; docking; nummularic acid; p53; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mapelli P., Ghezzo S., Samanes Gajate A.M., Preza E., Brembilla G., Cucchiara V., Ahmed N., Bezzi C., Presotto L., Bettinardi V. Preliminary Results of an Ongoing Prospective Clinical Trial on the Use of 68Ga-PSMA and 68Ga-DOTA-RM2 PET/MRI in Staging of High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients. Diagnostics. 2021;11:2068. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11112068. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

