Antimicrobial Activity of Quercetin: An Approach to Its Mechanistic Principle
- PMID: 35458691
- PMCID: PMC9029217
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27082494
Antimicrobial Activity of Quercetin: An Approach to Its Mechanistic Principle
Abstract
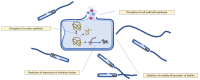
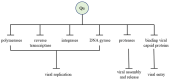
Quercetin, an essential plant flavonoid, possesses a variety of pharmacological activities. Extensive literature investigates its antimicrobial activity and possible mechanism of action. Quercetin has been shown to inhibit the growth of different Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria as well as fungi and viruses. The mechanism of its antimicrobial action includes cell membrane damage, change of membrane permeability, inhibition of synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, reduction of expression of virulence factors, mitochondrial dysfunction, and preventing biofilm formation. Quercetin has also been shown to inhibit the growth of various drug-resistant microorganisms, thereby suggesting its use as a potent antimicrobial agent against drug-resistant strains. Furthermore, certain structural modifications of quercetin have sometimes been shown to enhance its antimicrobial activity compared to that of the parent molecule. In this review, we have summarized the antimicrobial activity of quercetin with a special focus on its mechanistic principle. Therefore, this review will provide further insights into the scientific understanding of quercetin's mechanism of action, and the implications for its use as a clinically relevant antimicrobial agent.
Keywords: antibacterial; antifungal; antimicrobial activity; antiviral; mechanism of action; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jaisinghani R.N. Antibacterial properties of quercetin. Microbiol. Res. 2017;8:13–14. doi: 10.4081/mr.2017.6877. - DOI
-
- Kim S.J., Kim G.H. Quantification of Quercetin in different parts of onion and its DPPH radical scavenging and antibacterial activity. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2006;15:39–43.
-
- Ozgen S., Kilinc O.K., Selamoglu Z. Antioxidant Activity of Quercetin: A Mechanistic Review. Turk. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2016;4:1134–1138. doi: 10.24925/turjaf.v4i12.1134-1138.1069. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases