microRNA-4701-5p protects against interleukin-1β induced human chondrocyte CHON-001 cells injury via modulating HMGA1
- PMID: 35459188
- PMCID: PMC9034483
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-022-03083-8
microRNA-4701-5p protects against interleukin-1β induced human chondrocyte CHON-001 cells injury via modulating HMGA1
Erratum in
-
Correction: microRNA-4701-5p protects against interleukin-1β induced human chondrocyte CHON-001 cells injury via modulating HMGA1.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Apr 9;20(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05731-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40205613 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
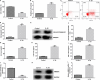
Background: miRNA-4701-5p has been reported to be a vital regulator in many diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, and miRNA-4701-5p is evidenced to be participated in synovial invasion and joint destruction. In our report, we investigated the roles of miRNA-4701-5p in osteoarthritis (OA) and analyzed the molecular mechanism.
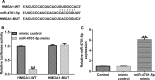
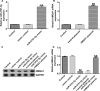
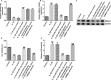
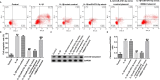
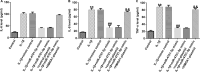
Methods: Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) was applied for stimulating human chondrocyte CHON-001 cells to establish an OA injury model. mRNA levels and protein expression were measured using qRT-PCR and western blot assay, respectively. The proliferation ability and cytotoxicity of CHON-001 cells were checked using MTT assay and lactate dehydrogenase activity. The inflammation of chondrocytes was accessed by the secretion levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. The apoptosis of chondrocytes was determined by flow cytometry assay. Bioinformatics software Starbase v2.0 analyzed the functional binding sites between miRNA-4701-5p and HMGA1 and the interaction was further confirmed using dual luciferase reporter analysis.
Results: miRNA-4701-5p was down-regulated in the IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes and HMGA1 directly targeted miRNA-4701-5p. Up-regulation of miRNA-4701-5p could alleviate IL-1β-treated CHON-001 cells inflammation and apoptosis, and reversed the cell proliferation decrease and cytotoxicity increase after IL-1β treatment. Nevertheless, all the roles of miRNA-4701-5p overexpression in CHON-001 cells could be reversed by HMGA1 up-regulation.
Conclusions: miRNA-4701-5p could alleviate the inflammatory injury of IL-1β-treated CHON-001 cells via down-regulating HMGA1, indicating that miRNA-4701-5p/HMGA1 is a promising therapeutic target for OA.
Keywords: Chondrocytes; HMGA1; Osteoarthritis; miRNA-4701-5p.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CircRNA circ-IQGAP1 Knockdown Alleviates Interleukin-1β-Induced Osteoarthritis Progression via Targeting miR-671-5p/TCF4.Orthop Surg. 2021 May;13(3):1036-1046. doi: 10.1111/os.12923. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33675175 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA XIST protects chondrocytes ATDC5 and CHON-001 from IL-1β-induced injury via regulating miR-653-5p/SIRT1 axis.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020 Mar-Apr;34(2):379-391. doi: 10.23812/19-549-A-65. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020. PMID: 32517436
-
Exosome-mediated circ_0001846 participates in IL-1β-induced chondrocyte cell damage by miR-149-5p-dependent regulation of WNT5B.Clin Immunol. 2021 Nov;232:108856. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2021.108856. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34536574
-
Long non-coding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 protects chondrocytes ATDC5 and CHON-001 from IL-1β-induced inflammation via regulating miR-138-5p/SIRT1.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):1445-1456. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1905247. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 33942704 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of circ-PRKCH alleviates IL-1β-treated chondrocyte cell phenotypic changes through modulating miR-502-5p/ADAMTS5 axis.Autoimmunity. 2022 May;55(3):179-191. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2022.2027918. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Autoimmunity. 2022. PMID: 35352613
Cited by
-
MiR-98-5p plays suppressive effects on IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury associated with osteoarthritis by targeting CASP3.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Apr 13;19(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04628-9. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 38615043 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HAGLR silencing inhibits IL-1β-induced chondrocytes inflammatory injury via miR-130a-3p/JAK1 axis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Mar 15;18(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03661-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36918905 Free PMC article.
-
Trigonelline Shields Chondrocytes from Oxidative Damage in Osteoarthritis through Activation of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Jul;197(7):4586-4601. doi: 10.1007/s12010-025-05232-1. Epub 2025 May 5. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40323359
-
HMGA1 Regulates IRS2 to Promote Inflammatory Responses and Oxidative Stress Injury in MPP+-Induced cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Mar;83(1):783-792. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01510-7. Epub 2024 Sep 8. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39244689
-
The role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Int Orthop. 2023 Aug;47(8):1895-1919. doi: 10.1007/s00264-023-05847-1. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Int Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37294429 Review.
References
-
- Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H, Carr AJ. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376–87. - PubMed
-
- Charlier E, Deroyer C, Ciregia F, Malaise O, Neuville S, Plener Z, Malaise M, de Seny D. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:49–65. - PubMed
-
- Blagojevic M, Jinks C, Jeffery A, Jordan KP. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2010;18(1):24–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

