Non-starch polysaccharide degradation in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chickens fed commercial-type diets supplemented with either a single dose of xylanase, a double dose of xylanase, or a cocktail of non-starch polysaccharide-degrading enzymes
- PMID: 35462208
- PMCID: PMC9048112
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101846
Non-starch polysaccharide degradation in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chickens fed commercial-type diets supplemented with either a single dose of xylanase, a double dose of xylanase, or a cocktail of non-starch polysaccharide-degrading enzymes
Abstract
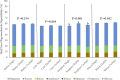
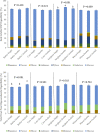
The aim of this study was to examine non-starch polysaccharide (NSP) degradation in the gastrointestinal tract of chickens fed a range of commercial-type diets supplemented with a commercial dose of xylanase, a double dose of xylanase or a cocktail of NSP - degrading enzymes. Cobb 500 broilers (n = 1,080) were fed 12 dietary treatments; 4 diets with differing primary grain sources (barley, corn, sorghum, and wheat) and three different enzyme treatments (commercial recommended dose of xylanase (16,000 BXU/kg), a double dose of xylanase (32,000 BXU/kg) or an NSP-degrading enzyme cocktail (xylanase, β-glucanase, cellulase, pectinase, mannanase, galactanase, and arabinofuranosidase at recommended commercial levels). There were 108 pens, approximately 10 birds per pen, 9 replicates per dietary treatment. The diets were fed as 3 phases, starter (d 0-12), grower (d 12-23), and finisher (d 23-35). On bird age d 12, 23, and 35, performance (total pen body weight, feed intake, and feed conversion ratio corrected for mortality [cFCR]), litter and excreta dry matter content, and ileal and total tract soluble and insoluble NSP degradability and free oligosaccharide digestibility was determined. On d 35, the quantity of NSP in the gizzard, jejunum, ileum and excreta was determined. Results from this study showed that the double xylanase dose and NSP-ase cocktail had positive impacts on starter phase performance in birds fed the corn- and wheat-based diets. In the grower phase in birds fed the barley-based diet, these enzyme treatments improved cFCR and increased litter dry matter content. The NSP-ase cocktail had a negative impact on finisher phase cFCR in birds fed the sorghum-based diet. The double xylanase dose induced a positive impact on NSP degradability and free oligosaccharide digestibility. In conclusion, there appears to be advantages to feeding broilers a double xylanase dose, but lack of consistency when using an NSP-ase cocktail containing many enzymes.
Keywords: enzyme cocktail; grains; non-starch polysaccharide; xylanase.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dietary soluble non-starch polysaccharide level and composition influences grower and finisher phase performance, excreta moisture content and total tract nutrient digestibility in broilers.Br Poult Sci. 2021 Oct;62(5):759-770. doi: 10.1080/00071668.2021.1919995. Epub 2021 May 12. Br Poult Sci. 2021. PMID: 33896287
-
Comparing the efficacy of stimbiotic and a combination of xylanase and beta-glucanase, in broilers fed wheat-barley based diets with high or low AME.Poult Sci. 2021 Oct;100(10):101383. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101383. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Poult Sci. 2021. PMID: 34438325 Free PMC article.
-
Performance, intestinal microflora, and amino acid digestibility altered by exogenous enzymes in broilers fed wheat- or sorghum-based diets.J Anim Sci. 2017 Feb;95(2):740-751. doi: 10.2527/jas.2016.0411. J Anim Sci. 2017. PMID: 28380608 Clinical Trial.
-
Xylanase supplementation in corn-based swine diets: a review with emphasis on potential mechanisms of action.J Anim Sci. 2020 Nov 1;98(11):skaa318. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa318. J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32970148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A perception that the feed grain basis of reduced-crude protein diets modifies the anabolic impact of insulin on the growth performance of broiler chickens.Anim Nutr. 2025 Mar 27;21:245-255. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.10.009. eCollection 2025 Jun. Anim Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40487105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Improving the Quality of Wheat Flour Bread by a Thermophilic Xylanase with Ultra Activity and Stability Reconstructed by Ancestral Sequence and Computational-Aided Analysis.Molecules. 2024 Apr 22;29(8):1895. doi: 10.3390/molecules29081895. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38675714 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Different Doses of Multienzyme Supplementation on Growth Performance, Duodenal pH and Morphology, and Carcass Traits in Broilers Fed Diets with an Increasing Reduction in Energy.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jul 21;13(14):2378. doi: 10.3390/ani13142378. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508155 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary multienzymes on the growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, nutrient digestibility, excreta noxious gas emission, and nutrient transporter gene expression in white feather broilers.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae133. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae133. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 38733150 Free PMC article.
-
Effects supplementation of novel multi-enzyme on laying performance, egg quality, and intestinal health and digestive function of laying hens.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104461. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104461. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39504823 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of phytase and xylanase enzymes on growth performance and Mucin2 gene expression in broiler chickens.Vet Med Sci. 2023 May;9(3):1241-1248. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1113. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36913214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aftab U., Bedford M.R. The use of NSP enzymes in poultry nutrition: myths and realities. World. Poult. Sci. J. 2018;74:277–286.
-
- Bach Knudsen K.E. The nutritional significance of dietary fibre analysis. Anim. Feed. Sci. Tech. 2001;90:3–20.
-
- Bautil A., Verspreet J., Buyse J., Goos P., Bedford M.R., Courtin C.M. Age-related arabinoxylan hydrolysis and fermentation in the gastrointestinal tract of broilers fed wheat-based diets. Poult. Sci. 2019;98:4606–4621. - PubMed
-
- Bedford M.R. Exogenous enzymes in monogastric nutrition-their current value and future benefits. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2000;86:1–13.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

