Hydroxamate and thiosemicarbazone: Two highly promising scaffolds for the development of SARS-CoV-2 antivirals
- PMID: 35462235
- PMCID: PMC9014651
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105799
Hydroxamate and thiosemicarbazone: Two highly promising scaffolds for the development of SARS-CoV-2 antivirals
Abstract
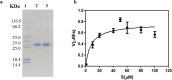
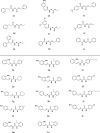
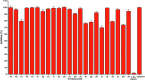
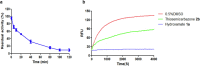
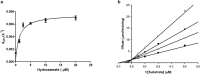
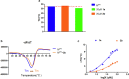
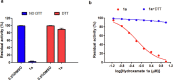
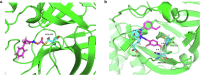
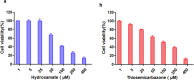
The emerging COVID-19 pandemic generated by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has severely threatened human health. The main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2 is promising target for antiviral drugs, which plays a vital role for viral duplication. Development of the inhibitor against Mpro is an ideal strategy to combat COVID-19. In this work, twenty-three hydroxamates 1a-i and thiosemicarbazones 2a-n were identified by FRET screening to be the potent inhibitors of Mpro, which exhibited more than 94% (except 1c) and more than 69% inhibition, and an IC50 value in the range of 0.12-31.51 and 2.43-34.22 μM, respectively. 1a and 2b were found to be the most effective inhibitors in the hydroxamates and thiosemicarbazones, with an IC50 of 0.12 and 2.43 μM, respectively. Enzyme kinetics, jump dilution and thermal shift assays revealed that 2b is a competitive inhibitor of Mpro, while 1a is a time-dependently inhibitor; 2b reversibly but 1a irreversibly bound to the target; the binding of 2b increased but 1a decreased stability of the target, and DTT assays indicate that 1a is the promiscuous cysteine protease inhibitor. Cytotoxicity assays showed that 1a has low, but 2b has certain cytotoxicity on the mouse fibroblast cells (L929). Docking studies revealed that the benzyloxycarbonyl carbon of 1a formed thioester with Cys145, while the phenolic hydroxyl oxygen of 2b formed H-bonds with Cys145 and Asn142. This work provided two promising scaffolds for the development of Mpro inhibitors to combat COVID-19.
Keywords: Hydroxamates; Inhibitor; Main protease; SARS-CoV-2; Thiosemicarbazones.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Farinholt T., Doddapaneni H., Qin X., Menon V., Meng Q., Metcalf G., Chao H., Gingras M.C., Avadhanula V., Farinholt P., Agrawal C., Muzny D.M., Piedra P.A., Gibbs R.A., Petrosino J. Transmission event of SARS-CoV-2 delta variant reveals multiple vaccine breakthrough infections. BMC Med. 2021;19:255. - PMC - PubMed
-
- A. Stern, S. Fleishon, T. Kustin, E. Dotan, M. Mandelboim, O. Erster, E. Mendelson, O. Mor, N.S. Zuckerman, (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

