A retrospective study of the efficacy of JAK inhibitors or abatacept on rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 35462572
- PMCID: PMC9135879
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-022-00936-w
A retrospective study of the efficacy of JAK inhibitors or abatacept on rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease
Abstract
Objectives: To examine the effectiveness of Janus-kinase inhibitors (JAKis) or abatacept (ABA) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD).
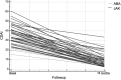
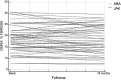
Methods: Patients with RA-ILD receiving JAKis or ABA were retrospectively evaluated at baseline and after 18 months of treatment. A computer-aided method (CaM) was used to assess the extent of high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) fibrosis percentage. According to HRCT fibrosis changes, patients were classified as "worsened" (progression of 15% or more), "stable" (changes within 15%) or "improved" (reduction of 15% or more). Correlations between RA characteristics and JAKis or ABA responses were studied using a multivariate regression model.
Results: Seventy-five patients (69.3% women) were evaluated, 31 received a JAKi while 44 received ABA. In the JAKis group, five patients (16.1%) showed RA-ILD progression, 20 patients (64.5%) were considered stable, and six patients (19.4%) demonstrated RA-ILD improvement. In the ABA group, five patients (11.3%) showed RA-ILD progression, 32 patients (72.7%) were stable, and seven patients (16.0%) demonstrated RA-ILD improvement. In both groups, the percentage of current smokers was different between those classified as "worsened" and those classified as "improved/stable" (p = 0.01). In multivariate regression analysis, current smoking habit (p = 0.0051) and concomitant methotrexate treatment (p = 0.0078) were the two variables related to RA-ILD progression in ABA-treated patients, whereas in JAKis-treated patients, the only RA-ILD progression-related variable was disease duration of RA (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Treatment with JAKis or ABA was related to stability or improvement of RA-ILD in 83.9% and 88.6% of patients, respectively. RA duration is the only variable associated with worsening RA-ILD in JAKis-treated patients.
Keywords: Abatacept; Baricitinib; High-resolution computed tomography; Interstitial lung disease; Janus-kinase inhibitors; Rheumatoid arthritis; Tofacitinib.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests to be declared.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
