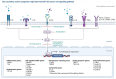
Sea Cucumber Compounds Targeting NF-κB in Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 35462875
- PMCID: PMC9019350
- DOI: 10.1177/11779322221091740
Sea Cucumber Compounds Targeting NF-κB in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
Cancer is a major health problem worldwide and the leading cause of death in many countries. It remains challenging to find anticancer treatments that work efficiently for varying types of cancer cells. Several studies revealed that nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a family of dimeric transcription factors that induce tumor promotion, progression, and therapeutic resistance, providing evidence that NF-kB may be a promising target for cancer drugs. Some research has found that sea cucumber biocompounds have anticancer properties, but further research is essential to confirm anticancer targets. This manuscript discusses the mechanisms of anticancer targeting the NF-κB signaling pathway induced by sea cucumber-derived compounds. Additional database analysis showed the protein targeted by the compounds involved in several pathways related to the NF-κB network. Moreover, SwissADME predicted druglikeliness properties of the active compounds of sea cucumber. The discussion is expected to provide new insight into the promising potential of these marine natural products for the treatment of many different types of cancers.
Keywords: Drug discovery; nuclear factor kappa B; pharmacokinetics; physicochemical; sea cucumbers.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Time course analysis of immunity-related gene expression in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus during exposure to thermal and hypoxic stress.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Dec;95:383-390. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.09.073. Epub 2019 Oct 1. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31585241
-
A Critical Transcription Factor NF-κB as a Cancer Therapeutic Target and its Inhibitors as Cancer Treatment Options.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(21):4117-4132. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666201111142307. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33176636 Review.
-
An updated review summarizing the anticancer potential of flavonoids via targeting NF-kB pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 6;15:1513422. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1513422. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39834817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chalepin: A Compound from Ruta angustifolia L. Pers Exhibits Cell Cycle Arrest at S phase, Suppresses Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB) Pathway, Signal Transducer and Activation of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Phosphorylation and Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathway in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Carcinoma (A549).Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Oct;13(Suppl 3):S489-S498. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_13_17. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 29142404 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Oncogenic Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling with Redox-Active Agents for Cancer Treatment.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Mar 10;30(8):1096-1123. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7387. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019. PMID: 29161883 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the NF-κB pathway as a potential regulator of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Feb 29;81(1):106. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-05098-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38418707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicity Effect of Holothuria Lessoni Sea Cucumber on Cancerous Mitochondria Obtained from Rat Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Oct 1;25(10):3717-3723. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.10.3717. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39471040 Free PMC article.
-
Sea cucumber-derived compounds for treatment of dyslipidemia: A review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 14;13:1000315. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1000315. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188620 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous